Fuses are an integral part of an electric circuit. They are responsible for the interruption and consequent stopping of overcurrent. All fuses have a metal wire or strip that melts or burns out when too much current occurs. As a result, this stops the overflow current from damaging the remaining parts of the circuit. There are two types of fuses available today: fast-blow fuses and slow-blow fuses. A fast blow fuse is the most common in household appliances. These fuse blocks overflow current from shorting out electrical devices and appliances.
Fast-blow fuses are fast-acting and burst immediately with any hint of an overflowing current. On the other hand, slow blow fuses can withstand high current overflow over a short period without bursting.
Contents
The Fast Blow Fuse Vs. Slow Blow Fuse

Electrical fuse
Now that you have a proper definition of a fast-blow fuse and a slow-blow fuse. Let us look at the differences between the two.
Use Cases
The first difference between these two types of fuses is their use. Slow-blow fuses are popular in the motor industry. They have proven to be a go-to over the years because of their properties. When turning on a motor engine, a high electric current flows through the circuit.
With this in mind, you need a fuse that can withstand the brunt of the current without blowing. Hence a slow-blow fuse. Moreover, this enables the motor to start without risking the fuse blowing.
Home appliances or small motors categorically use fast-blow fuses. Since most home appliances are sensitive to changes in electric currents, fast-acting fuses are the best option. As a result, a fast-blow fuse has a quicker reaction to counter any electric overflow.

Car fuses
Fuse Speed
The second difference is fuse speed. The time taken when the fuse is first open to catch the overflow current is fuse speed.
There are four main fuse speeds, and these apply to either fast or slow blow fuses. These fuse speeds also create four different fuse categories. These are:
Dual-Element Fuse
Dual-element fuses or time delay elements are very similar to slow-blow fuses. A multi-element provides short current protection, high performance, and a reliable overflow balance.
Fast Acting Fuse
A fast-acting fuse or a general application fuse protects sensitive electrical components. In hindsight, this fuse protects cables from melting or catching fires when an electrical overload occurs. This fuse is also a fast blow fuse or a general-purpose fuse.
Slow-Acting Fuse
Slow-acting fuses or time-delay fuses temporarily allow current overflow through a circuit. Short-acting fuses are motor start fuses. All slow fuses will, however, open and stop current over time. Slow fuses either accommodate or handle surge currents and temporary current overloads.
Ultra-Rapid Fuse
An ultra-rapid or semiconductor fuse is a short circuit in diodes, transistors, or thyristors. Semiconductor fuses operate at very high temperatures, providing a limited capability to protect against low overcurrent.
Consequently, ultra-rapid fuses use low melting point alloys. Ensure the fuse's I²t value is less than the electric device it will protect during purchase.
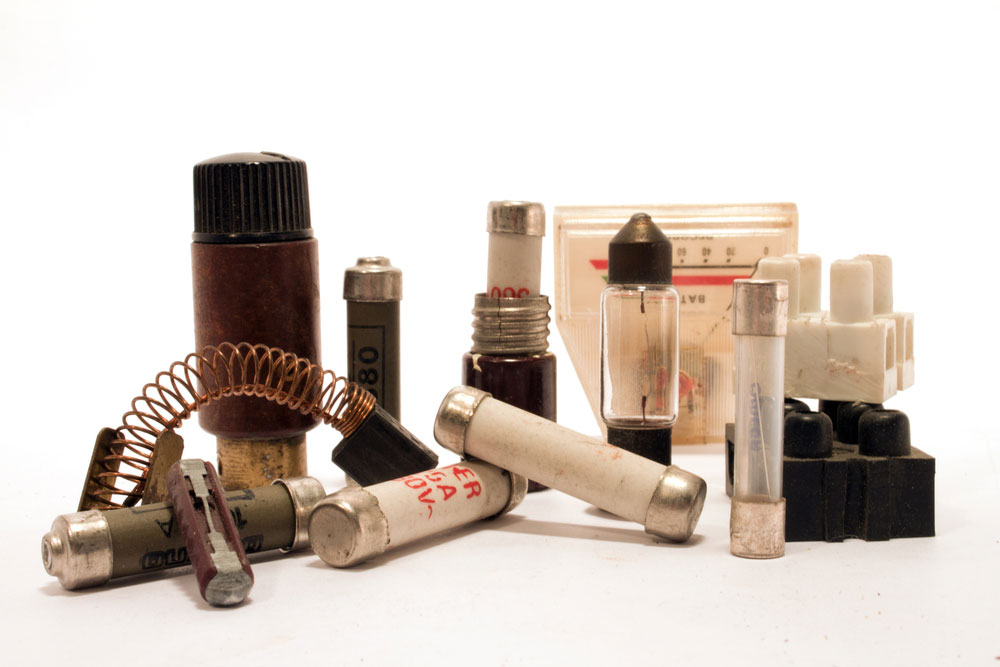

Various fuses
Here is a simple chart to help you determine the type of fuse. The fuse can either be ultra, fast, slow or dual-element.
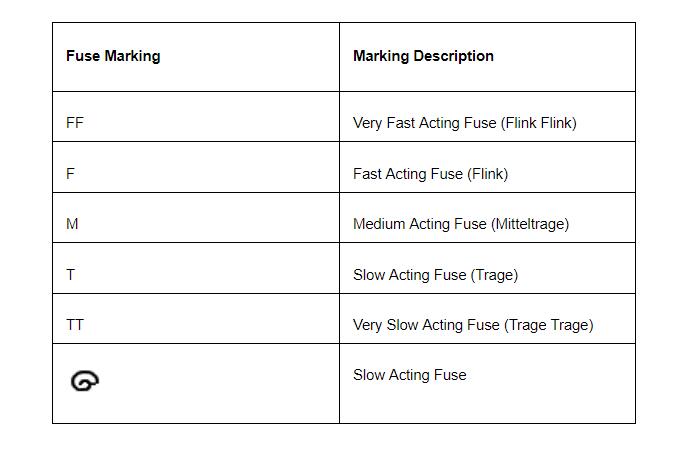
Fuse marking description chart
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
How To Tell If A Fuse Is A Fast Or Slow Blow?

Fuse box
For the most part, a fuse is a sacrificial element in a circuit. It either suffers and survives the brunt of an overflowing current or burns out.
When looking to replace a fuse, you must get the right one. How can you tell if the fuse is a fast-blow fuse or a slow-blow fuse?
Here is a step-by-step instruction guide to help you determine if a fuse is a fast or slow blow fuse.
Step 1
Firstly, look for a sticker or label around the fuse. The label on the fuse is the manufacturer's label, which will indicate fuse speed.
Step 2
The manufacturer's label should read either fast or slow. Look for the markings in the chart above to determine the speed of the fuse. Also, look for other markings or letters unique to your device or appliance.
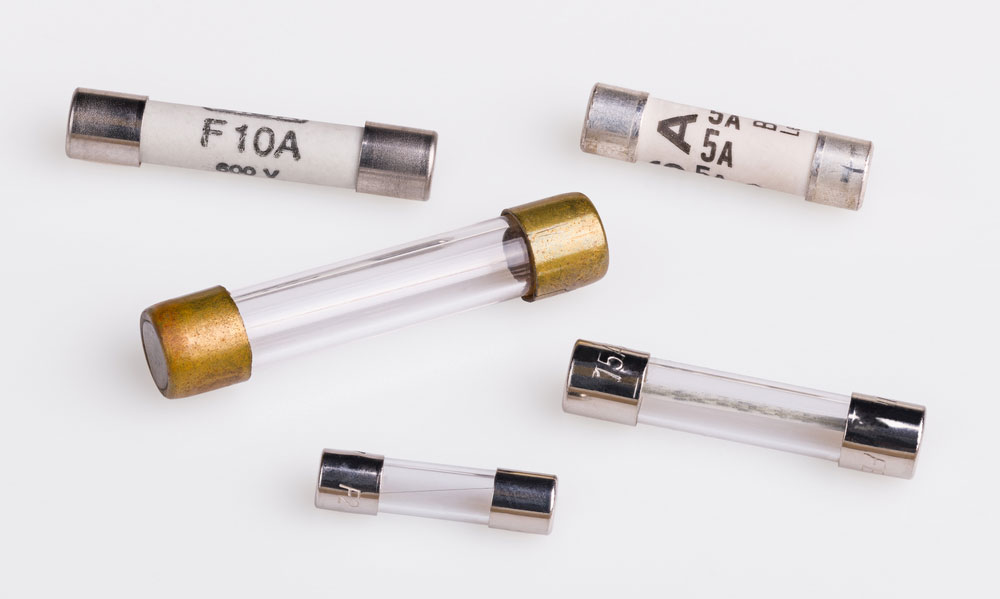

The label on the fuses
Step 3
With the speed check, now feel the fuse for raised lettering. For most fuses, this is on the fuse cap.
You should resort to this method if the marking and lettering on the fuse label are not legible. The imprinted letter on the cap indicates the speed of the fuse.
Step 4
For this step, you may need a magnifying lens. Using a magnifying lens, check the fuse to identify brand details and other manufacturer details.
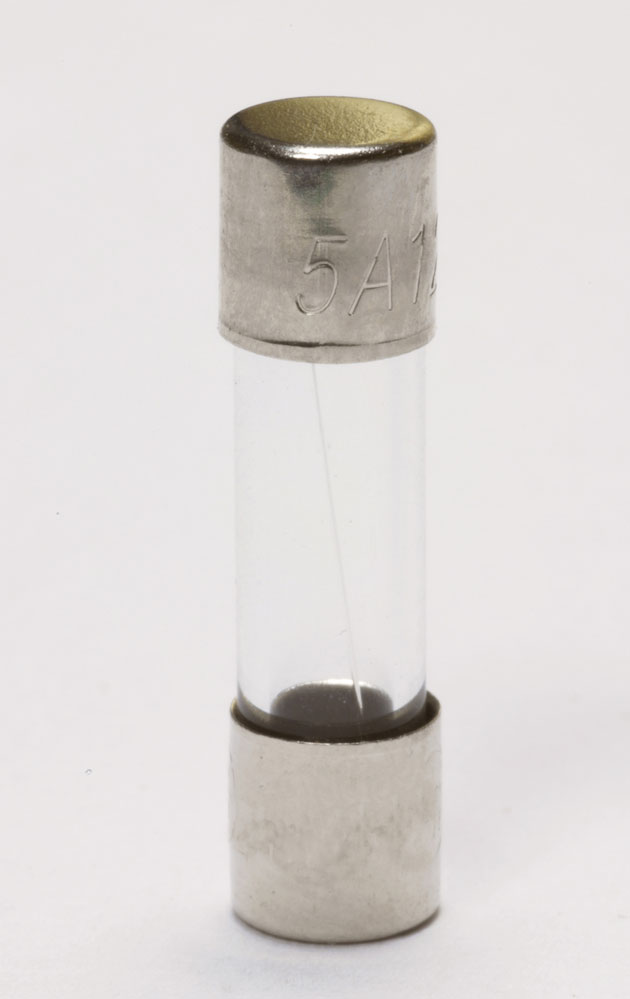

5 amp fuse details
Step 5
Now that you have all the fuse details, it is time to make a metal identification. Looking through the glass tubing, check for the wire filament. If the filament is thin, you look at a fast blow fuse.
And lastly, if the filament wire is thick and has a small spring at the end, you are looking at a slow blow fuse. Slow blow fuses have thicker filaments and a spring attached to one end.
How To Select A Suitable Fuse?
While both a slow-blow fuse and a fast-blow fuse do the same job, they are inherently different. Furthermore, the distinct structure and build make all the difference. Here is a step-by-step process of selecting a suitable fuse.
Step 1
The first step to selecting a suitable fuse is identifying the type of voltage you want to protect. Manufacturers not only rate fuses by voltage, but they also rate the DC and AC voltage.
You will get some fuses with dual rates, meaning they can work for DC and AC. However, the ratings on the fuses differ regarding the overall power use. Thus, selecting a fuse that does not fall into your circuit's voltage and power range may be catastrophic.
Step 2
Once you select a fuse based on the voltage, you want to observe your circuit's amperage. Your circuit's amperage is mostly what the fuse will be protecting. The observation applies to all courses, including motor and fluorescent lighting.
Select a fuse that is specific to your circuit. This will allow all the fuses to shield and protect the course from inrush current overload.
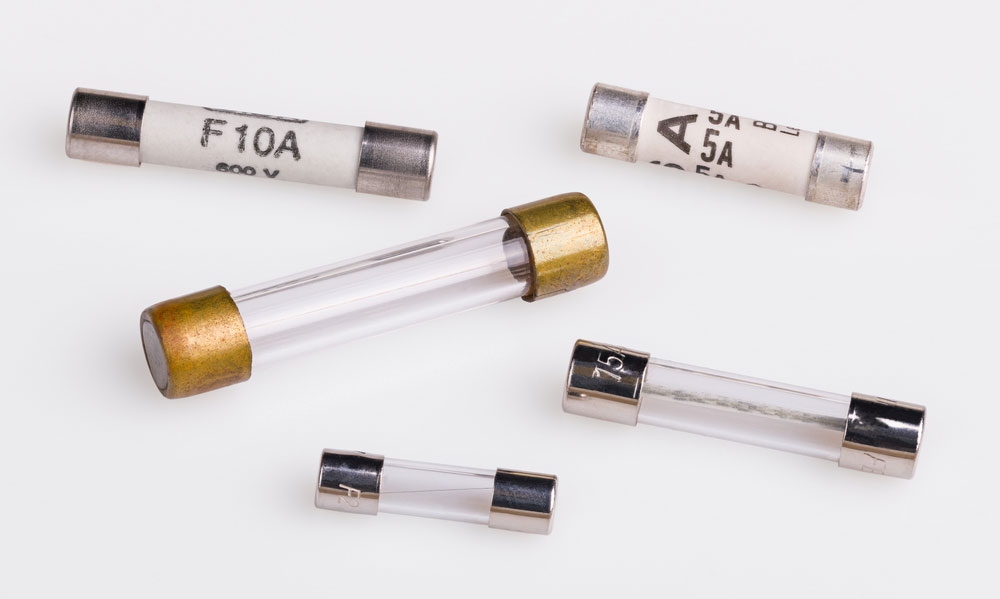

Set of miniature electrical fuses for overcurrent protection
Step 3
With the voltage and amperage sorted, you can select the fuse based on size. Ensure the fuse you choose fits in the fuse holder you are using. While at this, make sure the fuse holder you are using is specific to the fuse you will use.
Step 4
Some fuses available in the market today offer you the flexibility to replace the burnt-out part. Before replacing your fuse as a whole, check to confirm if you can return the burnt-out element. Doing this saves you the hustle of replacing the entire fuse.
Generally, conductive metals make most fuse elements. With this in mind, most of these elements are replaceable. When doing this, be careful not to damage the cartridge.
Step 5
Try to get a fuse with an inspection window when buying a fuse. These windows allow you to inspect whether or not your fuse has blown. Observation windows come in handy when finding out if your circuit is experiencing other issues.
Conclusion

Overloaded circuit board with a blown fuse
It is straightforward to overlook fuses and consider them trivial. However, in the absence of one, you have more to lose. Although miniature fuses are integral in ensuring your appliance and devices are safe from electric current overload.
More and more people are experimenting with PCBs. It is only fitting that you make sure fuses are always part of your requirement list. In conclusion, if you want more insights on this topic, do not hesitate to contact us.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!






