The semiconductor industry plays a critical role in all sectors of the economy because semiconductors are the basis of computers. However, the industry would not exist without the semiconductor PCB because it's the backbone or base for mounting semiconductor components.
Therefore, the semiconductor PCB is responsible for the explosive growth and development of modern computers. You will find it in almost all devices, such as mobile phones, GPS & navigation systems, LEDs, etc. Since it is an integral part of technology, we have looked at semiconductor PCBs in detail below. Read on to learn more!
Contents
What is Semiconductor PCB?
A semiconductor is a material that can act both as a conductor and insulator. Under the right conditions, a semiconductor can be a conductive material. This state is preferable in situations that require a controlled/regulated amount of electrical power, such as in the following:
- Integrated circuits
- Bipolar transistors
- LEDs
- Semiconductor PCBs
Therefore, a semiconductor PCB has a semiconductor as the base material on which other electronic components and semiconductor devices connect. Most semiconductor PCBs are relatively small compared to regular PCBs, making them ideal for small appliances, like smartwatches.
Difference Between Semiconductor PCB and IC
The main difference is the size. An integrated circuit is a tiny chip containing a set of electrical circuits on a flat piece of semiconductor material. Usually, it has millions of transistors and sits on the PCB surface to connect to the board's electrical components.
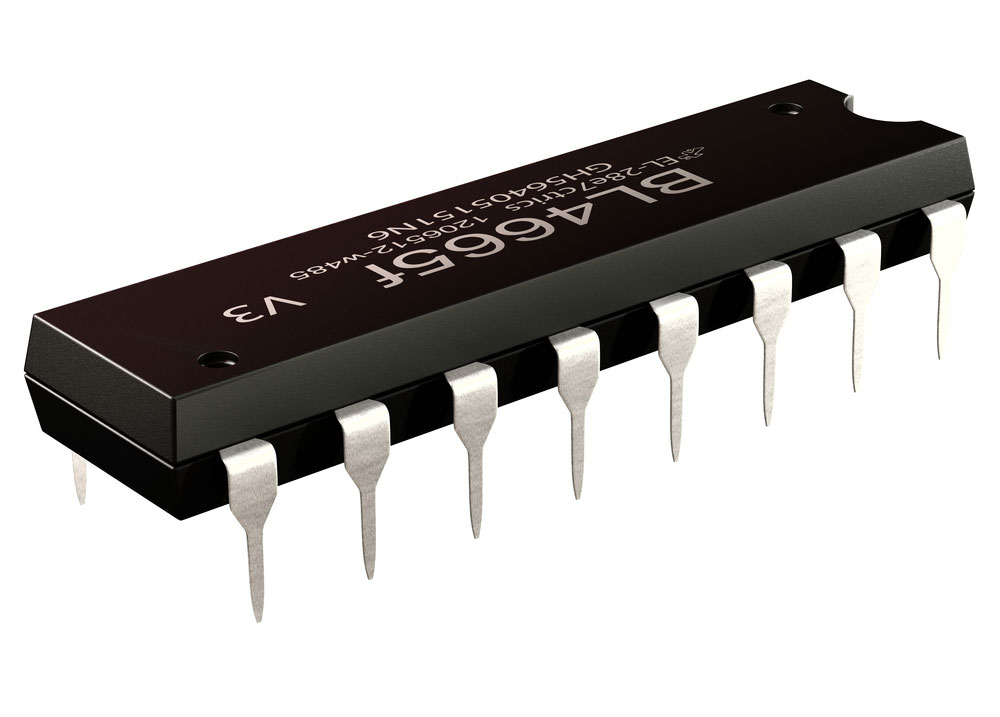
An integrated circuit
On the other hand, a semiconductor PCB is a larger, wider circuit. It provides mechanical support to all the semiconductor components mounted on board, such as the IC. The board also offers electrical connectivity and sometimes cooling to the entire PCB assembly.
The manufacturing process for semiconductor PCBs and ICs is slightly different from size. But both require a silicon wafer to start.
Silicon wafers in production
Benefits of Semiconductor PCB
- Cheaper than vacuum tubes
- It fits in most devices due to its small size.
- Makes shockproof electronic devices with longer lifespans
- Less noisy than vacuum tubes
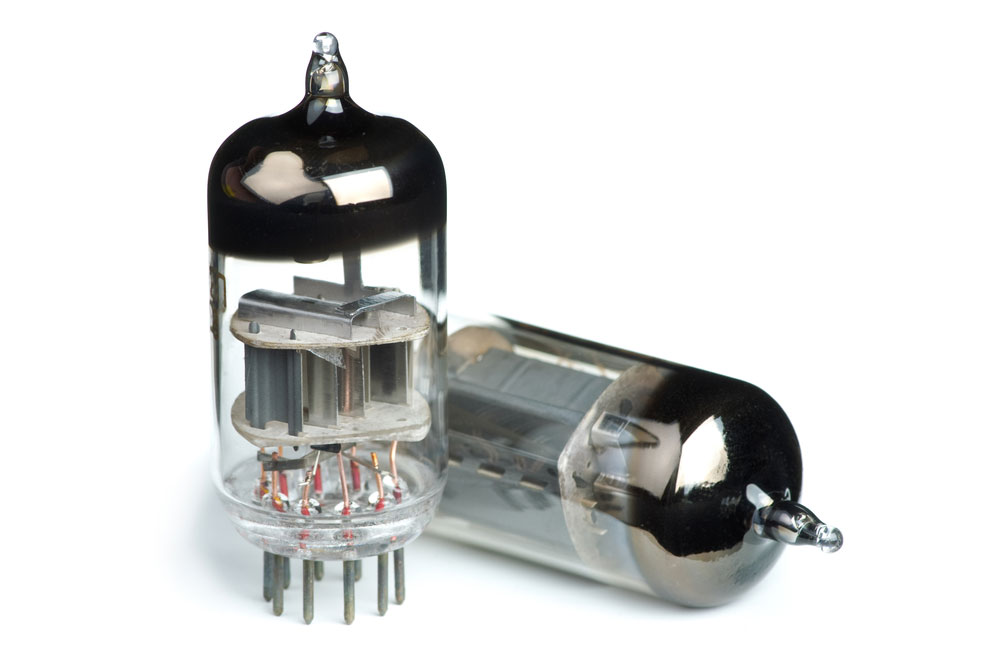

Vacuum tubes
- Capable of directing the flow of electrical signals
- Compact with quick and efficient performance
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
Semiconductor PCB Materials
Silicon is the most commonly used material to make semiconductors and semiconductor PCBs. Why? Silicon is a common element found almost everywhere on Earth. It takes up 27.7% of the Earth's crust, making it the second most abundant element, right after oxygen.
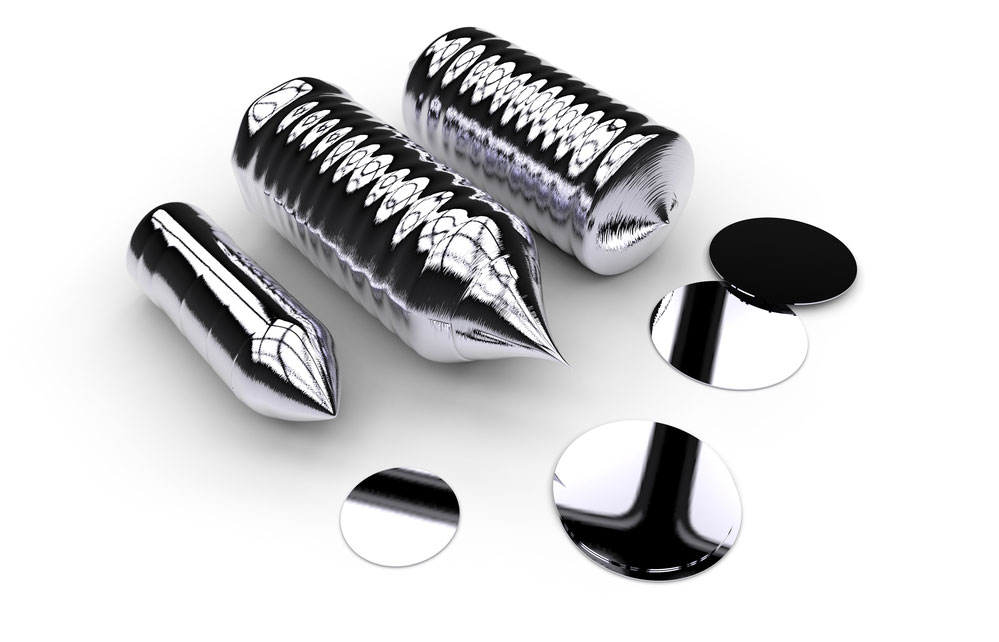

Silicon material
Therefore, it is cheaper to extract and does not require heavy processing. Also, it has an ideal working temperature range. These benefits make silicon the most researched and studied material in the electronics industry.
However, it is not the only semiconductor. Another popular one is Germanium. It has high thermal conductivity, making it perfect for heat-sensitive devices.

Germanium material
But it is uncommon to find a single material used in the manufacture of semiconductor PCBs. Most engineers create an alloy of Germanium and silicon to fuse the favorable properties of each one.
Germanium Arsenide is another popular material used to manufacture semiconductor PCBs for high-speed devices.
However, producing Germanium Arsenide is more costly than silicon because the latter has smaller wafers.
Therefore, some in the semiconductor industry combine the silicon-Germanium alloy with Germanium Arsenide. It minimizes costs while achieving the desirable properties of all three.
In addition to the semiconductor materials, the PCBs contain etched copper tracks to enhance electrical conductivity.
On the other hand, the substrate material can either be ABF, BT, or Epoxy resin. But the semiconductor material takes up most of the composition.
Semiconductor PCB Fabrication
- Deposition
- Removal (wet or dry etching)
- Patterning
- Modification of electrical properties
- Front End Of Line (FEOL) processing
- Gate oxide and implants
- Back End Of Line (BEOL) processing
- Metal layers
- Interconnect
- Wafer test
- Device test
- Die preparation

Printed circuit board manufacturing
Semiconductor PCB Prototyping
- Sourcing
- Solder paste stenciling
- Pick and place
- Reflow soldering
- Inspection and quality control
- Insert through-hole components
- Functionality test
Types of Semiconductor Printed Circuit Boards
- Single-Sided Semiconductor PCB
- Double-Sided Semiconductor PCB
- Multilayer Semiconductor PCBs
- Rigid Semiconductor PCB
- Flexible Circuit Semiconductor PCB
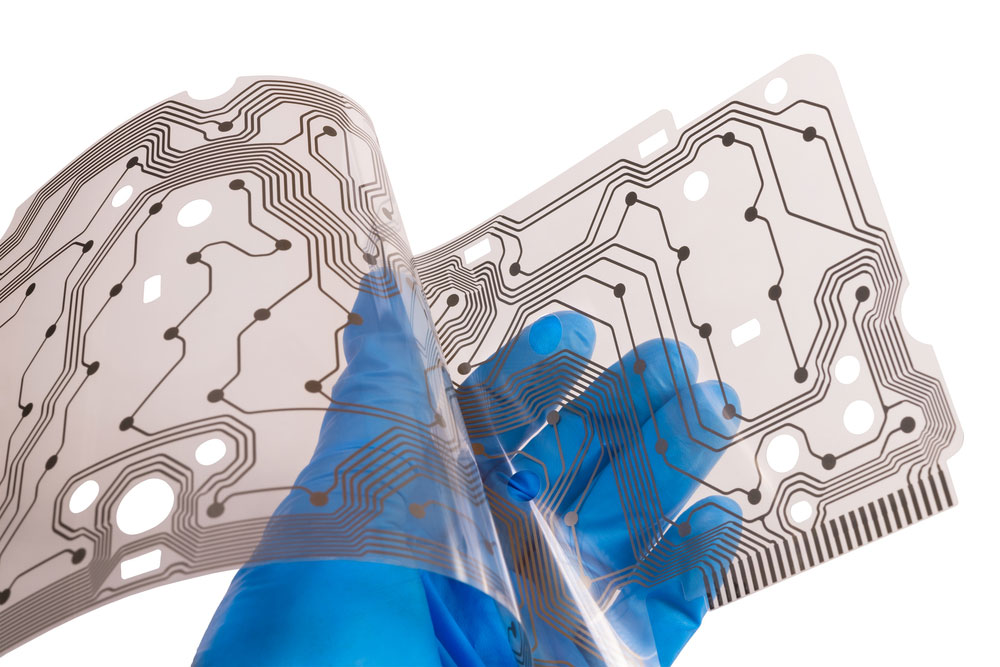
A flexible PCB
- Rigid-Flex PCB Semiconductor
Application and Use of Semiconductor PCBs
- Audio and video equipment
- Computers & Mobile phones & Smartwatches
- Navigation equipment
- Radio and radar systems

Radar systems
- Global Positioning Systems
- Communication equipment
- Digital displays
- LED systems
Summary
In conclusion, semiconductor PCBs are the basis of modern-day computers and are in almost every device. Therefore, whichever project you are working on, you will most likely need the semiconductor circuit board at some point in the process.
When that time comes, you can reach out to get the circuitry made at a reasonable price. At OurPCB, we have the three Es (expertise, experience, and equipment) to get the job done. Therefore, we will deliver a high-quality circuit board that meets all industry standards.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!