At OurPCB, we help you choose the right PCB laminate for optimal performance. PCB laminate forms the base of every circuit board, providing structure and insulation. In this article, we cover the key materials and types of laminates to guide your selection.
Contents
- What is Laminate in PCB?
- Types of PCB Laminates: Materials, Features, and Applications
- Importance of PCB Laminate
- PCB Material Properties Consideration
- PCB Laminate Material Properties Consideration
- Chemical Properties
- Mechanical Characteristics
- Thermal Properties
- Electrical Properties
- What to Consider When Selecting PCB Material
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What Is the Process of PCB Lamination?
- What Is the Difference Between Prepreg and Laminate PCB?
- What Causes PCB Delamination?
- Can You Use Different Laminate Materials Within the Same PCB Design?
What is Laminate in PCB?
PCB laminate is the base material used in the construction of PCBs. It typically comprises multiple layers of fiberglass, epoxy resin, or other insulating materials, bonded together under high pressure and temperature. This composite structure not only supports the components mounted on the PCB but also ensures the durability and stability of the board during operation.
Types of PCB Laminates: Materials, Features, and Applications
What types of PCB laminates are available? Common options include FR4 for insulation, flexible laminates for adaptability, high-frequency laminates for fast signals, metal-core for heat dissipation, and ceramic for thermal stability. Rogers, BT epoxy, and halogen-free laminates offer specialized performance for specific applications.
PCB laminates vary based on the materials used, offering different features suited to specific applications:
| Type of Laminate | Material | Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR4 Laminate | Fiberglass cloth & epoxy resin | Affordable, strong, good electrical insulation | General-purpose electronics, consumer devices |
| Flexible Laminates | Polyimide or polyester | Thin, flexible, adaptable to movement | Wearable devices, medical equipment |
| High-Frequency Laminates | PTFE, ceramic composites | Low dielectric loss, handles high-speed signals | Telecommunications, radar systems |
| Metal-Core Laminates | Aluminum or copper base | Superior heat dissipation, high thermal conductivity | LED lighting, power electronics |
| Ceramic Laminates | Ceramic-filled composites | High thermal stability, excellent insulation | Military electronics, satellite communication |
| Rogers Laminate | Ceramic or PTFE-based | Superior high-frequency performance | 5G infrastructure, aerospace systems |
| BT Epoxy Laminates | Bismaleimide-triazine (BT) resin | Better thermal performance, low moisture absorption | Automotive, mobile devices |
| Halogen-Free Laminates | Halogen-free materials | Environmentally friendly, good thermal properties | Eco-friendly products, consumer electronics |
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
Importance of PCB Laminate
Choosing the right PCB laminate is crucial for the functionality and reliability of a printed circuit board. Laminates influence several key performance characteristics:
- Electrical Performance: PCB laminates impact the electrical properties, including signal integrity, dielectric loss, and impedance control. A stable dielectric constant in the laminate minimizes signal distortion, vital for high-speed and RF applications.
- Thermal Management: Effective heat dissipation is necessary to prevent damage to components. Laminates with high thermal conductivity, like metal-core laminates, manage heat efficiently, enhancing the lifespan and performance of the board, especially in high-power applications.
- Mechanical Strength: The mechanical strength of the laminate ensures the PCB can withstand physical stress during manufacturing, assembly, and operation without cracking or warping, which is critical for multi-layer or heavy-component boards.
- Environmental Durability: Laminates designed for harsh environments can withstand high humidity, extreme temperatures, or exposure to chemicals, maintaining PCB performance without degradation.
- Cost Efficiency: The choice of laminate can affect production costs. High-frequency laminates may be more expensive but are necessary where performance cannot be compromised. FR4 laminates offer a cost-effective solution for general-purpose electronics.
- Flexibility: In designs requiring flexibility, such as wearable technology, flexible laminates allow the PCB to bend and conform to various shapes without breaking, while still maintaining performance.

PCB Material Properties Consideration
PCB Laminate Material Properties Consideration
When selecting PCB laminate materials, it's essential to consider specific properties critical to your application. Below are key characteristics to evaluate:
Chemical Properties
- Moisture Absorption: The amount of water vapor a material can absorb. This affects the dimensional stability of the PCB.
- Flammability: The ability of the material to resist catching fire. The industry uses the UL 94 Vertical Burn Test to classify PCB materials.
- Methylene Chloride Resistance: Resistance to methylene chloride, a common solvent in PCB manufacturing. It's important as some materials can be dissolved by this chemical.
Mechanical Characteristics
- Density: Affects the weight and thickness of the PCB.
- Time to Delamination: The time it takes for the material to begin to delaminate under specific conditions, affecting the board's durability.
- Peel Strength: The force required to peel the laminate from the PCB, indicating durability.
- Flexural Strength: The force required to bend the laminate, determining the PCB’s ability to withstand physical stress without breaking.
Thermal Properties
- Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE): Measures how much the material expands or contracts when exposed to heat, impacting thermal stability.
- Thermal Conductivity (k): Indicates the material's ability to conduct heat, crucial for managing heat dissipation.
- Decomposition Temperature (Td): The temperature at which the material begins to break down, affecting long-term reliability.
- Glass Transition Temperature (Tg): The temperature at which the material changes from rigid to flexible, affecting its performance under different thermal conditions.
Electrical Properties
- Dielectric Loss Tangent (Tan δ): Measures the material's ability to dissipate heat, affecting signal integrity.
- Dielectric Constant (Er): Reflects the material's ability to store energy, influencing the electrical performance of the PCB.
- Electrical Strength: Indicates the material's ability to withstand an electric field.
- Surface Resistivity (pS): Measures the material's resistance to the flow of electrical current across its surface.
- Volume Resistivity (p): Measures the resistance to electrical current throughout the material, calculated by multiplying surface resistivity by thickness.
What to Consider When Selecting PCB Material
- Cost: Balance cost with the other factors to find the best material for your project.
- Availability: Some materials are more readily available, which can impact cost and lead time.
- Performance: Consider thermal conductivities, dielectric constants, and other performance metrics.
- Lead Time: Ensure the material's lead time aligns with your project timeline.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Process of PCB Lamination?
Circuit board lamination involves placing the internal layers (prepregs and foils) under extreme pressure and temperature with a photosensitive dry resist in a vacuum heat press.
The PCB cures at high temperatures for some time, after which the material cools slowly, and pressure gets released gradually, resulting in a stack that forms a multi-layer PCB.
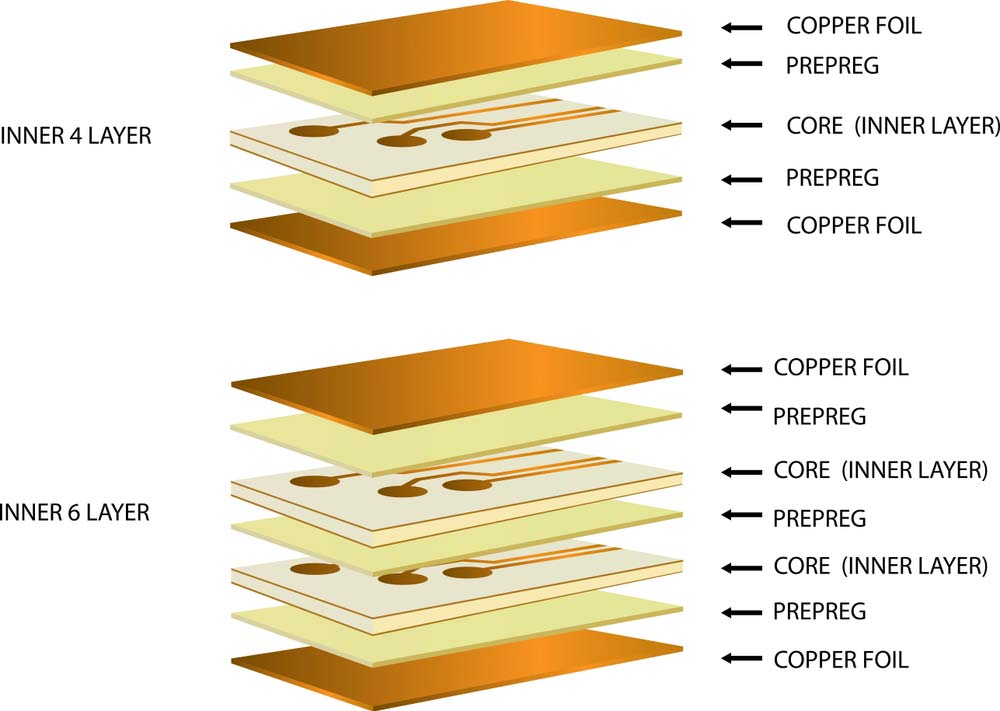
What Is the Difference Between Prepreg and Laminate PCB?
PCB laminates are the base or core materials that provide structural support to circuit boards and insulation between the copper foils or conductive layers. On the other hand, prepregs are insulation layers that can separate two cores (laminates) or a core and a copper layer.
What Causes PCB Delamination?
The root cause of delamination is trapped moisture between the layers. Improper storage of the base materials can make them absorb moisture, which will expand rapidly during lamination due to the high heat, causing delamination.
The separation can also occur during assembly because the soldering heat will expand the moisture, and the vapor must find a way out.
Can You Use Different Laminate Materials Within the Same PCB Design?
Yes, you can. However, you should consider the performance requirements for the different board sections to pick the most suitable core materials.
Back to Top: PCB Laminate Materials
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!