Many electronic devices use transistors, and the 2n2222 pinouts transistor is just one among the huge transistor family. The 2n2222 transistor can handle a higher current than other transistors and switch a load current of 800mA, which is often high compared to other transistors.
In this article, we will learn more about the features of the 2n2222 transistor, its alternatives, and more. It is essential because it will enable you to determine connections of the 2n2222 transistor in your circuits.
Let's start!
Contents
- What is a 2N2222 Transistor Pinout?
- Pin Configuration Description
- 2N2222 vs. 2N2222A: What’s the Difference?
- 2n2222 NPN Transistor Electrical Features
- Alternative Options and Equivalents
- Can I use BC547 instead of 2N2222?
- 2n2222 Package Introduction
- Basic 2n2222 Example Circuits
- An LED Controlling Circuit
- Configuring DC Motor as a Switch using Arduino
- How to Safely Long Run 2N2222 in a Circuit
- Applications of a 2n2222 NPN Transistor.
- 2n2222 Pinout FAQs
- What is the Function of the 2N2222 Transistor?
- How to use 2n2222 Pinouts?
- Summary
What is a 2N2222 Transistor Pinout?
2n2222 is an NPN bipolar junction transistor. Importantly, its uses are for analog frequency amplification and switching applications. The 2n2222 transistor amplifies signals by receiving an analog signal through the collectors, and the base gets another signal. For instance, this analog frequency could be a human voice. The TO-18 package encloses the main functional area of the 2N-2222 transistor. Moreover, its small size and efficiency make it the most preferred transistor in many electronic devices.
Pin Configuration Description
The 2n2222 transistor consists of 3 pins. Consequently, the transistor pins either turn it on or off. These pin configuration descriptions are below;
| PIN | Pin Name | Pin Function |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | Emitter Pin | This pin drains the current flowing to the transistor. |
| #2 | Base Pin | This pin controls the current of the emittor to the base. |
| #3 | Collector Pin | This pin provides the transistor current to the output load. |
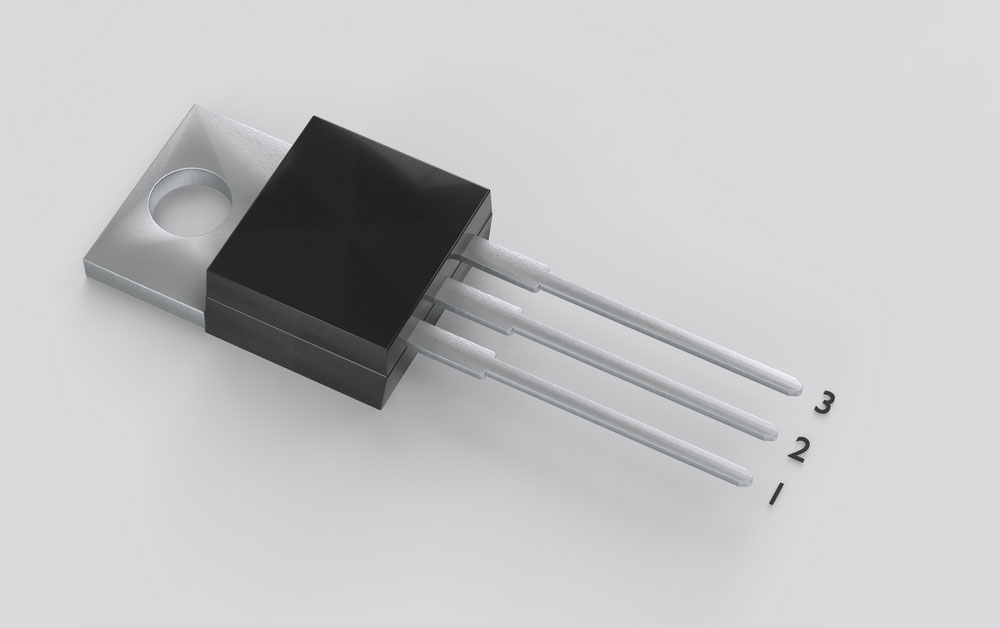
(2N2222 pinout diagram)
2N2222 vs. 2N2222A: What’s the Difference?
The names only have a single-letter variation, but these transistors have electrical, packaging, and cost differences.
Considering the electrical difference, the 2N2222 has higher maximum absolute ratings than the 2N2222 BJT transistor. The specific collector-to-base, collector-to-emitter, and emitter-to-base voltage ratings are 75V, 40V, and 6V, while the ratings for the 2N2222 are 60V, 30V, and 5V.
On the packaging, the 2N2222A has the TO-92 semiconductor package, a plastic or epoxy casing, while the 2N2222 has metal packaging resembling a metal can.
![]()
A BJT transistor with a plastic TO-92 semiconductor package
The cost goes hand-in-hand with the packaging because the plastic TO-92 makes 2N2222A transistors cheaper than the metal can 2N2222.
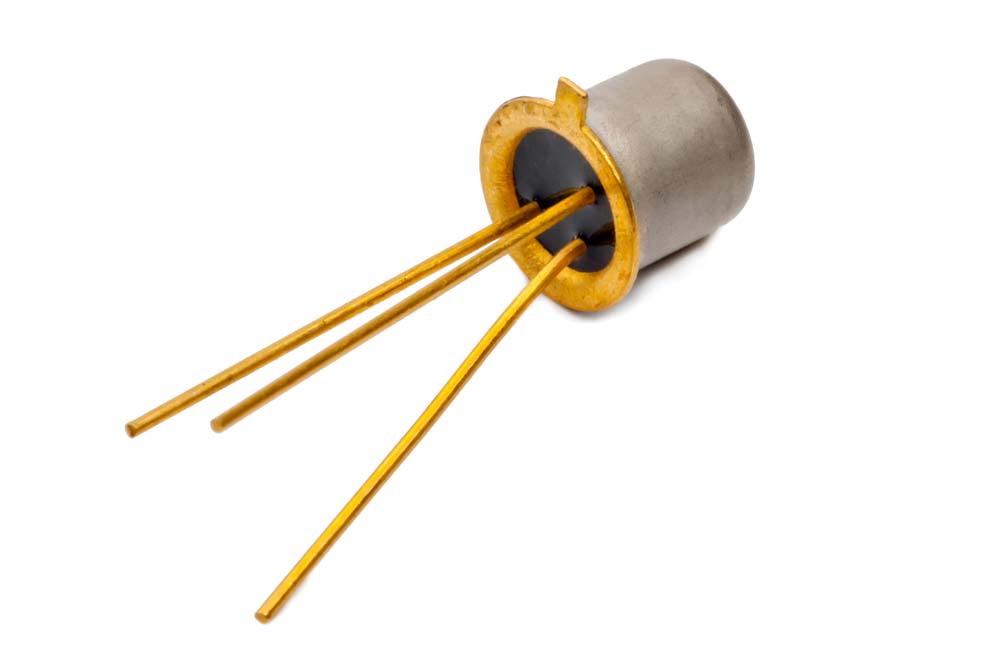

A BJT metal-case transistor
2n2222 NPN Transistor Electrical Features
The key features of a 2n2222 NPN transistor are;
- Gain (hFE): 100-300
- Collector-emitter saturation voltage (Vce sat): 0.3-0.5 volts
- Collector current (Ic): 0.1 amps
- DC Current gain (hfe): 60-150
- Collector power dissipation (Pc): 0.5 watts
- Frequency response: 0-1000 MHz
- Operating temperature (Tj), °C: -55 to +150
- Storage temperature (Tstg): -55 to +150
- Thermal resistance junction-to-ambient air (Rja): 80°C/W
- The Thermal resistance junction-to-case (Rjc): 90°C/W
- Thermal resistance junction-to-ambient air (Rja): 80°C/W
- Collector emitter breakdown voltage (V(beo)ce): 50 volts
- DC gain-collector to emitter (here): 100-300
- Collector-emitter saturation voltage (Vce sat): 0.5 volts
- Power transistor dissipation (Tc): 1 watt
- Collector-emitter voltage (Vce): 0.3 volts

(Transistors)
Alternative Options and Equivalents
There are many different types of transistors in the electronics world. For instance, the 2n2222 transistor has alternative options, such as the MPSA42 and the 2N3906. On the other hand, its equivalents are the KTN2222, BC637, BC547, PN2222, MPS2222, KN2222, 2N2907and 2N3904.
The 2n2222 transistor is equivalent to the bc547 transistor but slightly different because the pin configuration is reversed in the bc547 transistor pinouts.
A feature difference between the 2n2222 and the bc547 is that the 2n2222 transistor allows a collector current of up to 800mA. However, bc547 cannot power up to 800mA. Consequently, the power dissipation of a 2n2222 is 652mW and can power larger loads than the bc547.
(Different types of transistors)
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
Can I use BC547 instead of 2N2222?
Yes, you can. However, it is important to consider that the 2N2222 is more powerful than the BC547.
The 2N2222 transistor’s collector-to-base voltage is 60V, while that of the BC547 is 50V. Its collector-to-emitter voltage is higher, 45V compared to the 2N2222’s 30V. The emitter-to-base voltage is also slightly higher because it is 6V, while the 2N2222 rating is 5V.
When considering the maximum collector current, the 2N transistor’s rating is a whopping 800mA, while that of the BC is only 100mA.
Other critical performance factors are power dissipation, DC gain, thermal resistance, and transition frequency. The power dissipation rating is the same on both (500mw), so we’ll focus on the other three.

Different transistor types and radio components
2N2222 transistors have a DC gain of 75-300HFe, while the BC547 has a wider range and higher gain, from 110 to 800HFe. The thermal resistance of the 2N is 146k/w, while that of the BC is 83.3c/w.
Lastly, the transition frequency on the 2N is lower (250MHz) than that of the BC (300MHz), which means a lower noise figure of 4dB on the former. The noise figure for the BC is 10dB.
When making the electrical connections to the circuit, keep in mind the 2N has an emitter, base, and collector pinout, while the BC has a collector, base, and emitter pinout.
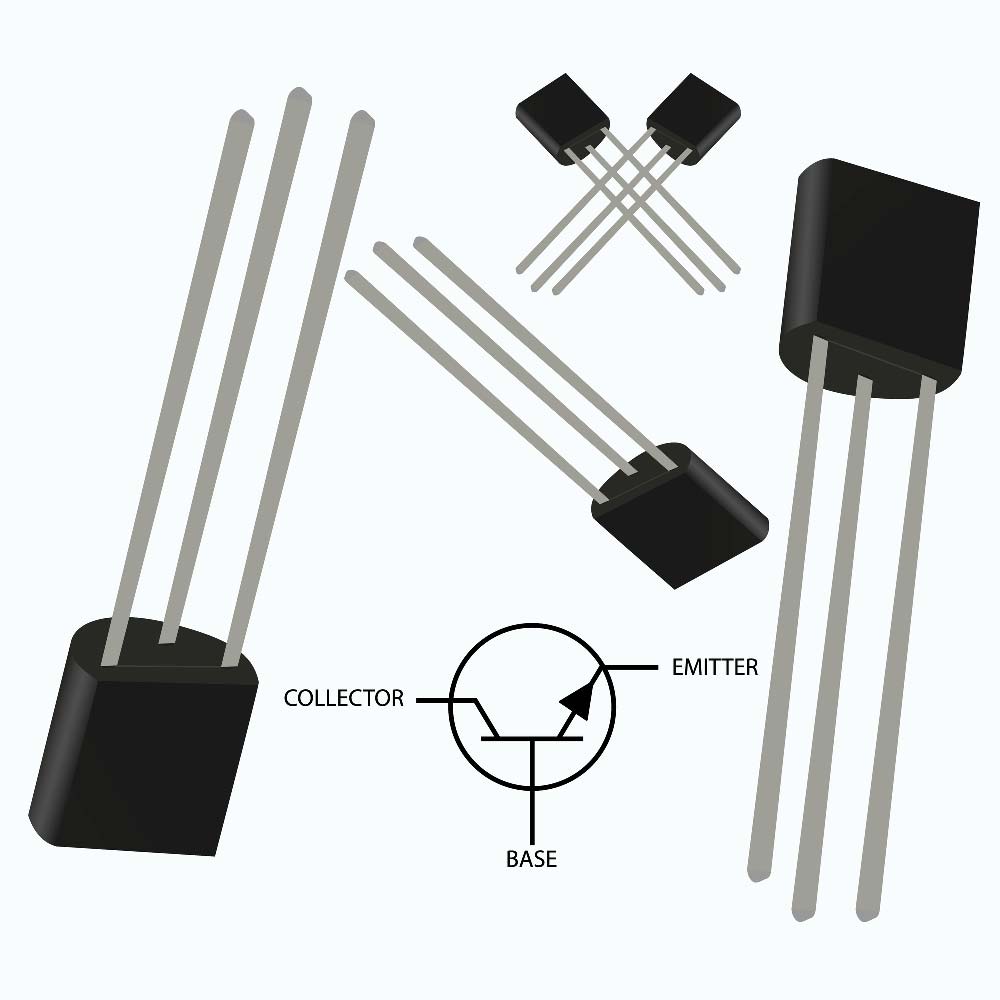

The three pins of an NPN transistor (2N2222)
You can consider the last difference as cosmetic. 2N BJTs come packaged in a TO-18 metal can package, while BC semiconductors have a plastic TO-82 package. So you can interchange the two because the performance stats are not very different.
2n2222 Package Introduction
Most importantly, the 2n2222 transistor package uses the TO-18 package, which is a design for transistor metal case style. In addition, the TO-18 package style of the casing is more expensive than the TO-92 package.
Transistors using 1,2 or 3 leads (not more than three) use the 3-lead TO-18 package. It is so because examples of LED, diodes, and photodiodes may use only two leaders. Light-emitting or light-sensitive diodes have a transparent window or parabolic reflector in the top of their case rather than a sealed flat top.
(Integrated circuit chip with a TO-18 package.)
Basic 2n2222 Example Circuits
Here, we discuss examples of NPN transistors connected in circuits. We have a simple LED controlling model with a switch and another important example to help you understand better!
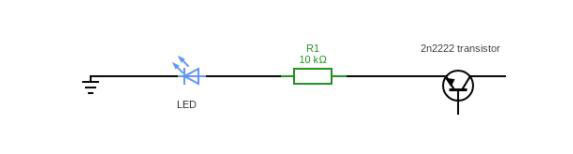
An LED Controlling Circuit
This circuit connects the base terminal and collector terminal to the power source through a 220ohm resistor.
(An LED Controlling Circuit)
It is an LED-controlling circuit that will not work without the 10kΩ resistor. In addition, if you use it, the switch won't turn on because of the low current passing. However, all should be well with this smaller value for resistors like a 220-ohm resistor between terminals and a 5-volt logic signal at base input (on/off)!
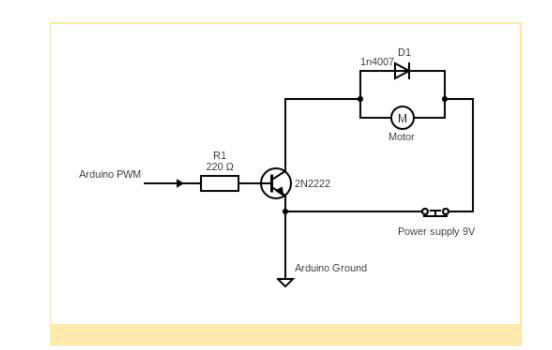
Configuring DC Motor as a Switch using Arduino
We will use our 2N2222 transistor and an Arduino board to interface our motor in this example. Importantly, this circuit can control any DC motors by switching implemented circuits with transistors as switches. Also, you may recognize these LED flashing drives from your car or home, which are used to turn things on/off quickly (and make them blink).
(Configuring DC motor as a switch using Arduino)
How to Safely Long Run 2N2222 in a Circuit
If you want this transistor to last long in your circuit while delivering the best performance, don’t drive more than 600mA into it.
Remember, its maximum collector current is 800mA, but you should keep it slightly lower to maximize durability. It would be best to use the appropriate base resistor to deliver the required current to the transistor’s base terminal.
On the other hand, the collector-to-emitter voltage should be under 40V. During storage, the temperature should not exceed 150°C and under -55°C.
Applications of a 2n2222 NPN Transistor.
- First, a vital application of this transistor is in high-power application systems.
- Second, it can perfectly fit in amplification applications.
- Also, it efficiently works when used in an inverter and other rectifier circuits.
- Lastly, it is usable in the Darlington transistors.
2n2222 Pinout FAQs
What is the Function of the 2N2222 Transistor?
A 2n2222 transistor amplifies low-power to high-power or works as a switch in switching applications.
How to use 2n2222 Pinouts?
A 2n2222 NPN transistor switches loads of higher current into low. Moreover, a 2n2222 transistor can work as a switch or an amplifier. Consequently, when used as a switch, the transistor allows a large current to flow through the collector. Also, it can flow a small current through the base.
Summary
2N2222 transistors are one of the most common transistors in the world today. It has a 3-pin configuration. Notably, their uses are rapidly growing in industrial applications, engineering projects, and many more. Meaning that 2n2222 transistors are here to stay.
We hope this article has answered some of your questions about this transistor. If you liked it, please check out more articles from us. For more information, do not hesitate to contact us!
Back to top: 2N2222 Pinouts Comprehensive Guide
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!