Batteries store electrical energy to power all kinds of devices. But what if you took advantage of an alternative, environmentally-friendly option for that same capability? A supercapacitor integrated into an electronic circuit provides the ideal solution! This particular capacitor type charges a lot more quickly than a lithium-ion battery. Not only that, but this passive element has unlimited charging cycles, which means it lasts for a long time. We provided an in-depth guide on this topic, so continue reading if you want to learn more about the Supercapacitor charging circuit!
Contents
- What is a Super Capacitor?
- Supercapacitor Charging Circuit
- Circuit diagram:
- Required components:
- Working principle:
- How to Charge a Super Capacitor?
- Applications
- FAQs:
- What is the difference between a capacitor and a supercapacitor?
- What is the fastest way to charge a supercapacitor?
- How long can a supercapacitor hold a charge?
- Can a supercapacitor replace a battery?
- Summary
What is a Super Capacitor?
A supercapacitor is a specially designed capacitor with significant energy storage and fast charging capabilities. However, it has less cell voltage rating, ranging from 1V to 5.5V, compared to regular capacitors. You can connect these capacitor types in series to generate high voltage for powerful equipment.
Supercapacitors can also store 10 to 100 times more energy per unit mass than an electrolytic capacitor. They also offer infinite charging and discharging cycles, whereas a lithium-ion battery begins deteriorating after a charging process. Thus, this component can easily last for more than ten years.
Compared to rechargeable batteries, a supercapacitor features low-charge density and quickly releases energy. Not only that, but it can charge in under a minute due to its low ESR (Equivalent series resistance). Also, integrating capacitors in series will boost the maximum charge voltage.
Supercapacitor Charging Circuit
Circuit diagram:
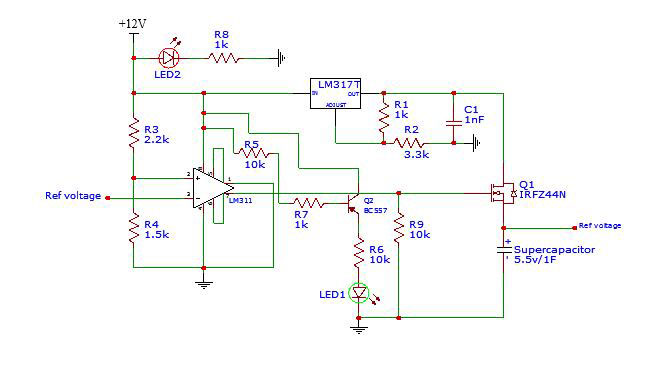
Supercapacitor charger circuit diagram.
Required components:
- 12V power supply
- LM311 IC – 1x
- LM317 voltage regulator IC – 1x
- IRFZ44N transistor – 1x
- BC557 PNP transistor – 1x
- LED – 2x
- 1k resistor – 3x
- 2.2k resistor – 1x
- 1.5k resistor – 1x
- 10k resistor – 3x
- 3.3k resistor – 1x
- 1nF capacitor – 1x
- 5.5v/1f super capacitor – 1x
Working principle:
Overall, a 12V adapter supplies power to the capacitor charger circuit. It features an LM317, which regulates 5.5V that charges the supercapacitor. However, a MOSFET, operating as a switch, distributes the 5.5V to the capacitor. If the capacitor voltage is under 4.86V, then the button closes. Otherwise, a higher voltage will cause the switch to open, stopping the charging process. An op-amp helps to measure and compare those voltage levels. Meanwhile, the BC557 transistor illuminates the LED whenever charging completes.
Both R1 and R2 resistors determine the LM317’s output voltage. In this case, it relies on the formula Vout = 1.25* (1+R1/R2). The circuit relies on the 1k and 3.3k values to regulate a 5.3V output voltage. An LM311 IC compares the supercapacitor’s voltage with the supply voltage level, distributing to pin two via a voltage divider circuit. Then, the 2.2k and 1.5k resistors decrease the voltage level from 12v to 4.86v. Afterward, the IC compares the reference voltage with the 4.86v. If the ref voltage reaches below 4.86v, pin seven will work with the 10k resistor to draw in more voltage. Afterward, the higher voltage powers the MOSFET.
Next, the IRFZ44N MOSFET connects to the supercapacitor, which gets charged through the op-amp signal. After the op-amp switches to a high state, its pin seven will output 12v, causing the MOSFET to activate through the base pin. Lastly, the BC557 transistor illuminates the LED once the MOSFET deactivates, which indicates that the supercapacitor’s voltage surpassed 4.8v.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
How to Charge a Super Capacitor?
You can charge a supercapacitor by connecting its positive and negative terminal to the power supply’s positive and negative end, respectively.
Applying more voltage than the supercapacitor’s limit can damage the component, so you should be cautious. In this case, ensure that the charging voltage exceeds 90% of the capacitor voltage rating. Otherwise, it could cause a thermal runaway. You can solve this issue by connecting a resistor in series with the supercapacitor and voltage source. Therefore, this implementation will reduce current flow levels through the capacitor, preventing damage. After it reaches a full charge, the current will decrease.
Each plate will generate a charge after connecting the supercapacitor to the DC voltage source. A double-layer electrolytic capacitor forms as a result of this charge.
Applications

An MP3 player features a supercapacitor.
Supercapacitors are ideal solutions for rapid charge and discharge cycles instead of long-term energy storage. The component integrates into a few of the applications listed below.
- MP3 players
- Buses
- Trains
- Cranes
- Elevators
- Static RAMs
- Wind turbines
- Professional-grade camera flashes
- Cell phones
- Laptops
- Electric cars
FAQs:
What is the difference between a capacitor and a supercapacitor?
A capacitor provides energy storage via an electric field supplied to the circuit as energy. Meanwhile, a supercapacitor stores its electrical energy between the charged electrode and electrolyte ions in a double layer.
What is the fastest way to charge a supercapacitor?
Connecting a regulated power supply to a supercapacitor will quickly charge the component in seconds. However, you will need to set the current rating of the RPS before continuing.
How long can a supercapacitor hold a charge?
A supercapacitor can hold a charge anywhere from microseconds to a few weeks. Of course, this depends on its leakage current and circuit resistance.
Can a supercapacitor replace a battery?
 Supercapacitors can replace a battery in various applications.
Supercapacitors can replace a battery in various applications.
Yes. Supercapacitors have already replaced vehicle and electronic device batteries to store an electrical charge.
Summary
Overall, a supercapacitor is an alternative energy storage solution for an electronic device. However, these do not possess the same features as rechargeable batteries. For example, the component has unlimited charging cycles, allowing it to last very long On the other hand, it releases energy quickly, which means it does not take long to drain the component. As a result, you may want to integrate additional supercapacitors in series to ensure they won’t drain as quickly.
Do you have any questions regarding the supercapacitor? Feel free to contact us!
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!