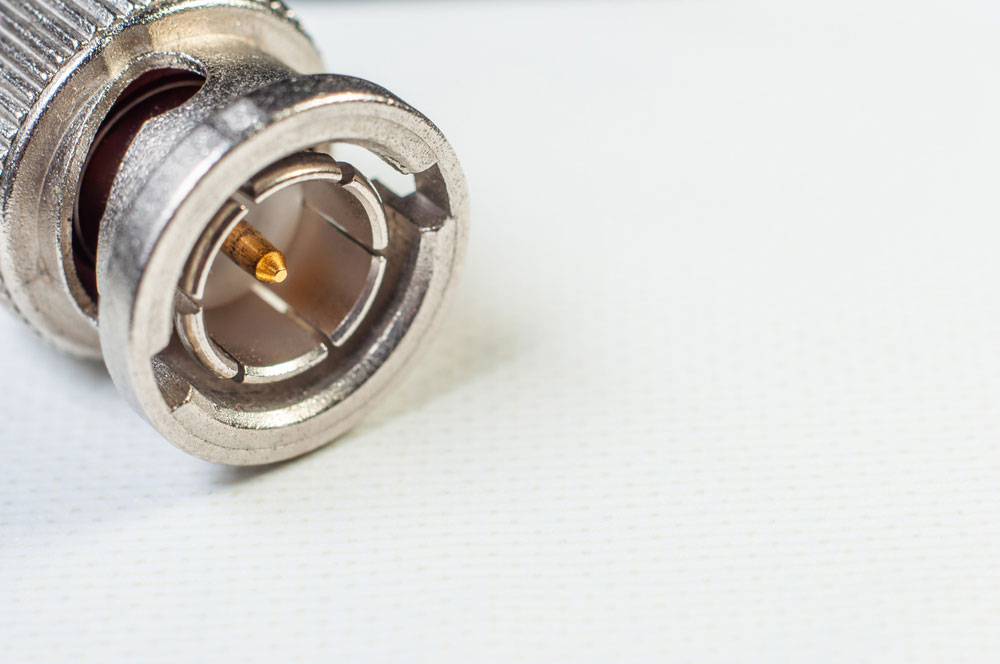
About SMA vs. BNC, When comparing connectors for RF transmission wires, there are different options at your disposal. They include type N, UHF, TNC, SMA, and BNC. The last two are more common in RF applications, and we’ll compare SMA vs. BNC to highlight their performance. Let’s get right into it!
Contents
What are SMA Connectors?
SMA (SubMiniature version A) is a semi-precision 50-ohm impedance connector that can operate up to 18 GHz. Some proprietary versions can operate at frequencies up to 26.5 GHz, but standard versions cap it at 18 GHz.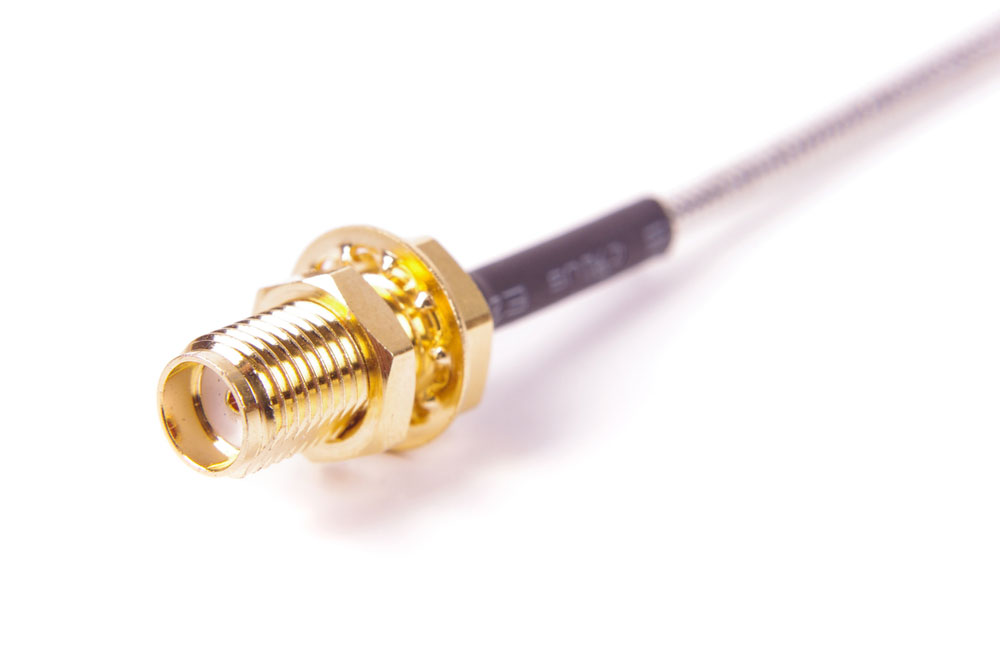 
A 50-ohm radio frequency coaxial cable with an SMA connector
The connectors come in various formats, including male and female, right-angled and straight-through, etc. These coaxial cable connectors are typical in high-frequency applications, such as the following.
- Mobile phone antennas
- RF isolators
- Wi-Fi router antennas
- Microwave systems
- RF power amplifiers
- Radio astronomy (at frequencies over 5 GHz)
- Handheld radio
- USB software-defined radio dongles
History
SMA connectors began as BRM (Bendix Real Miniature) connectors in the 1950s. James Cheal from Bendix Research Labs designed the connector, and its continued development by the lab incorporated it into MIL-C-39012.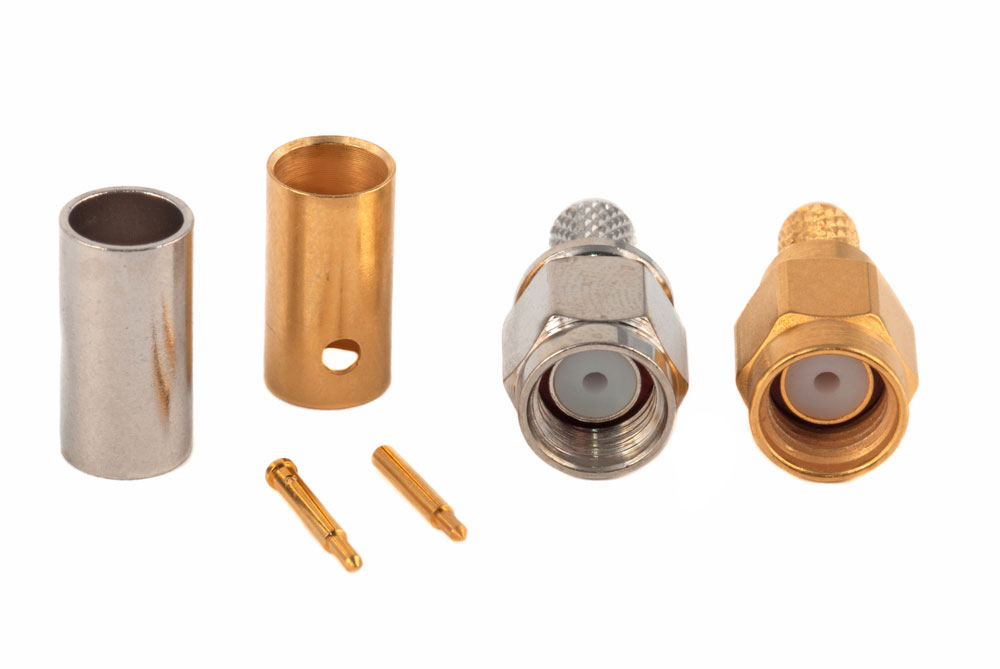 
High-frequency SMA connectors
This incorporation occurred in 1968, after which the connector received the SMA designation. The connector was originally for DC frequencies ranging from 0-12 GHz. But this got extended with variants handling 18-26.5 GHz. Mechanically compatible connectors like K connectors enable SMAs to operate up to 40 GHz.
SMA Connector Design
This coaxial connector features a threaded barrel with 36 threads per inch. And the barrel has a 1/4-inch diameter. Male SMA connectors have a 5/16-inch threaded nut, with the standard-polarity type bearing a 0.9mm diameter center pin. This pin has a surrounding barrel with inner threads. 
High-frequency, right-angled SMA connectors
On the other hand, the female SMA connector features a center sleeve surrounded by a barrel having outer threads. This gender differentiation corresponds to the orientation of the innermost component. But with the reverse-polarity SMA connectors, the male type features center sleeves surrounded by inner threaded barrels. On the other hand, female reverse-polarity SMA connectors have the center pin with outer threaded barrels.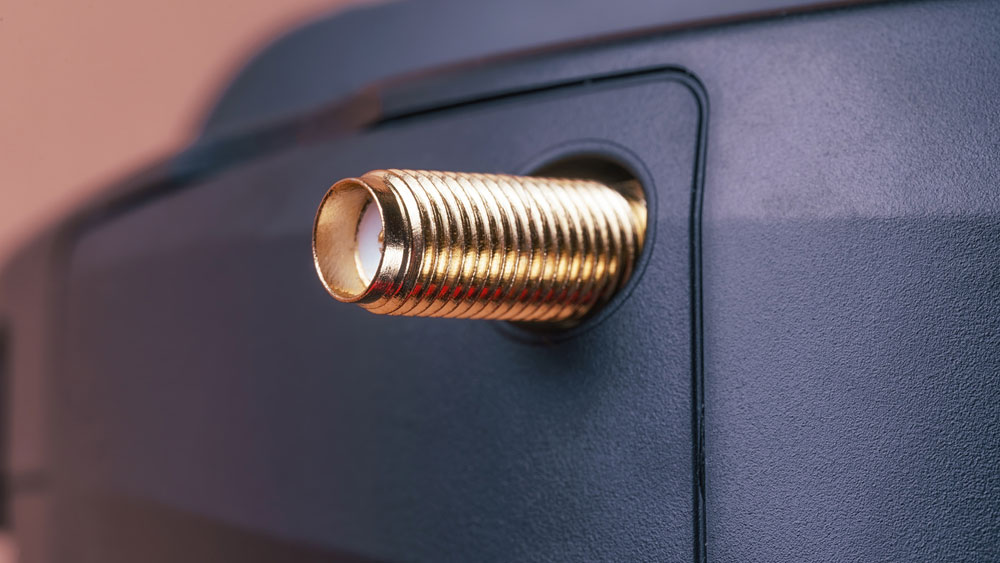 
A female SMA connector
Durability
SMA connectors usually have a 500-mating cycle rating, but this durability depends on the fastening torque. With stainless steel SMA connectors, set the torque of the fastening wrench to 0.8-1.1 Nm or 7-10 in-lbf. Brass is softer. So, brass connectors require 0.3-0.6 Nm or 3-5 in-lbf.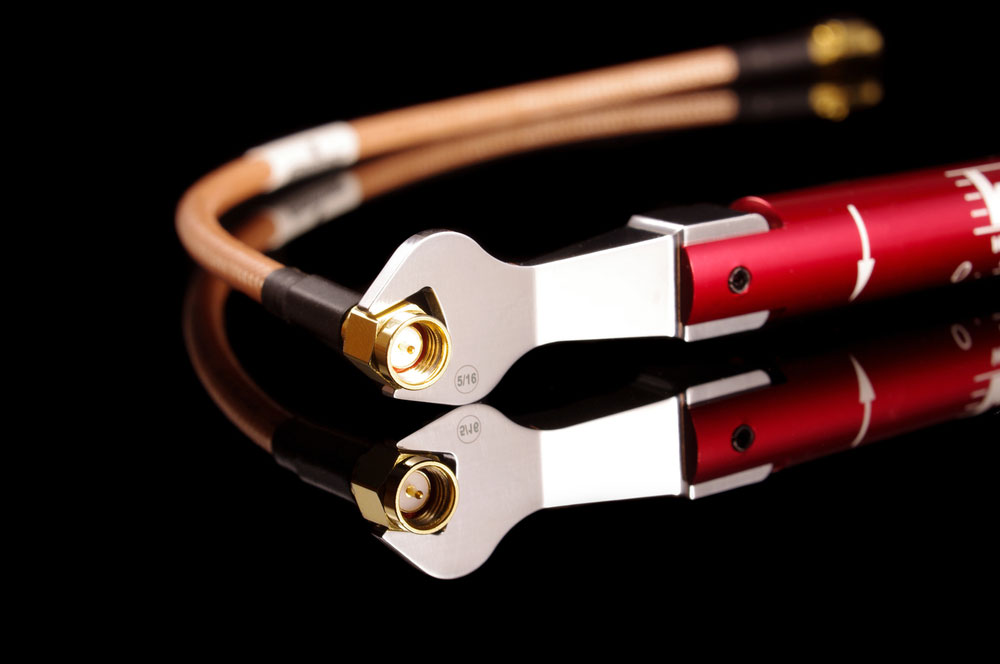 
A professional torque wrench for SMA connector tightening
Applying higher torque than recommended will weaken the connectors, reducing the mating cycles.
Dielectric
These SMA connectors have PTFE dielectrics with contacts on the mating plane. The connector’s mating and construction variability limits their impedance repeatability. This limitation caps their connection cycles.
Variations
As stated earlier, SMA connectors have a mode-free DC operation up to 18 GHz. But proprietary versions have ratings up to 26.5 GHz. However, you can get other connectors with higher frequency ratings. Technically, these connectors are SMA-like. And they include the 3.5mm connector. This variant has a rating of up to 34 GHz (free-mode performance).
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
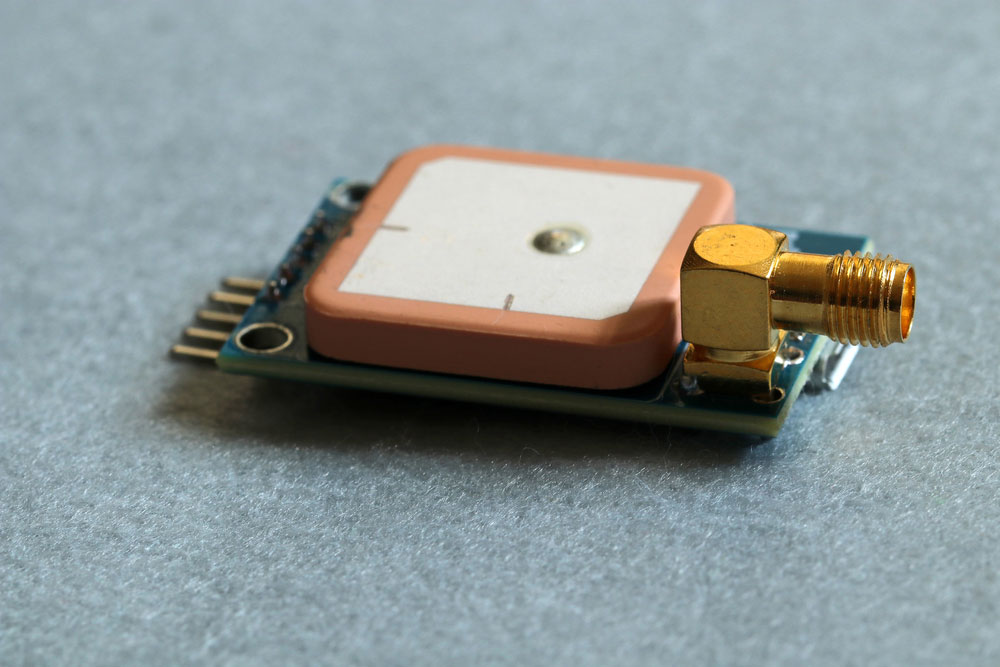
A GPS module with an SMA connector
The 2.9mm SMK or K-type is effective up to 46 GHz, making it ideal for high-performance components and measurement systems. These two achieve higher frequencies than regular SMA connectors because they have air dielectrics with center conductors appropriately scaled. The 2.9mm and 3.5mm refer to the inner diameter of their outer conductors. But their outer threads are similar to SMA connectors, hence the name SMA-like. So, you can cross-mate them.
What are BNC Connectors?
BNC (Bayonet Neill-Concelman) is a quick connect/disconnect, non-threaded, miniature RF coaxial cable connector with the same characteristic impedance as the coaxial cable. Therefore, it can either have a 50-ohm or 75-ohm characteristic impedance.
A BNC connector for transmitting audio and video signals
BNC Connector Design
This connector features a twist-to-lock mechanism. The female side contains two lugs that engage a slot on the male side to lock the two. Mating the two to full locking involves turning the coupling nut quarterway.
Dielectric
The male and female ends have outer conductors with plastic dielectric materials. Although efficient at low frequencies, this plastic dielectric increases data losses at high frequencies. If the transmission inside exceeds 4 GHz, the slots on the outer conductors can radiate the signals. This radiation makes the connector unstable and unusable. 
A BNC connector for signal electronics
You can find the BNC connector specifications referenced in the MIL-STD-348 standard.
BNC Connector Types
As stated earlier, this connector is available in 50 and 75-ohm types, with the latter having reduced or zero plastic dielectrics on the mating ends. This design makes 75-ohm BNC connectors suitable for transmitting frequencies up to 2 GHz, usually in HD video signal cables. Since the 50-ohm type has a thicker dielectric, it can handle frequencies up to 4 GHz, making it suitable for data transmission cables. 
BNC connectors for closed-circuit TV applications
Wrap Up
As you can see, SMA and BNC connectors have different benefits and drawbacks that make them suitable for different use cases. For instance, BNC connectors are ideal for audio and video streaming because they can only handle lower frequencies in coaxial cables. However, SMA connectors are better for internet data wire connections because they can handle higher frequencies. That’s it for now. Contact us if you need these connectors or circuit board assemblies for your project, and we’ll give you the best deals. See you in the next article.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!