Power Relay Module is one of the most simplistic components. However, they are also one of the most important. This is because they are the link between low-powered digital electronics and high-powered devices. They allow digital circuits and digital microcontrollers to switch high-powered devices on and off.
This guide will take a deep dive into relay modules and why they are so important. Maybe it will inspire you to integrate them into your next microcontroller or LED project. Without further ado…
Contents
What is a Relay Module?
 Relay microcontroller
Relay microcontroller
Relay modules (or power relay modules) are ubiquitous electronic components. They are an exceedingly significant component of any home automation project. You will require a relay module if you use a low voltage microcontroller such as an Arduino to control motors or lighting circuits.
Relay modules are straightforward components. Essentially, they work as switches. Your average relay module comprises two internal metal contacts. Usually, these contacts do not connect or touch each other. However, relays include an internal switch connecting these contacts to complete an electrical circuit that allows current flow.
Relay modules do not work like manual light switches. To illustrate, when you switch on a light, you must press a button to connect the two metal contacts within it. Inversely, a relay switch uses electric pulses to turn its internal switch on and off.
You power a voltage power current on one side of the circuit that powers an electromagnetic coil which pulls the metal contacts together. Consequently, this allows the current to flow on the other side of the relay. Your Arduino Uno or Raspberry Pi can send a digital signal to the relay, which can then power whatever application you need. As you may expect, there are different relay module types. We will cover that further down this guide.
How Do Relay Modules Work?
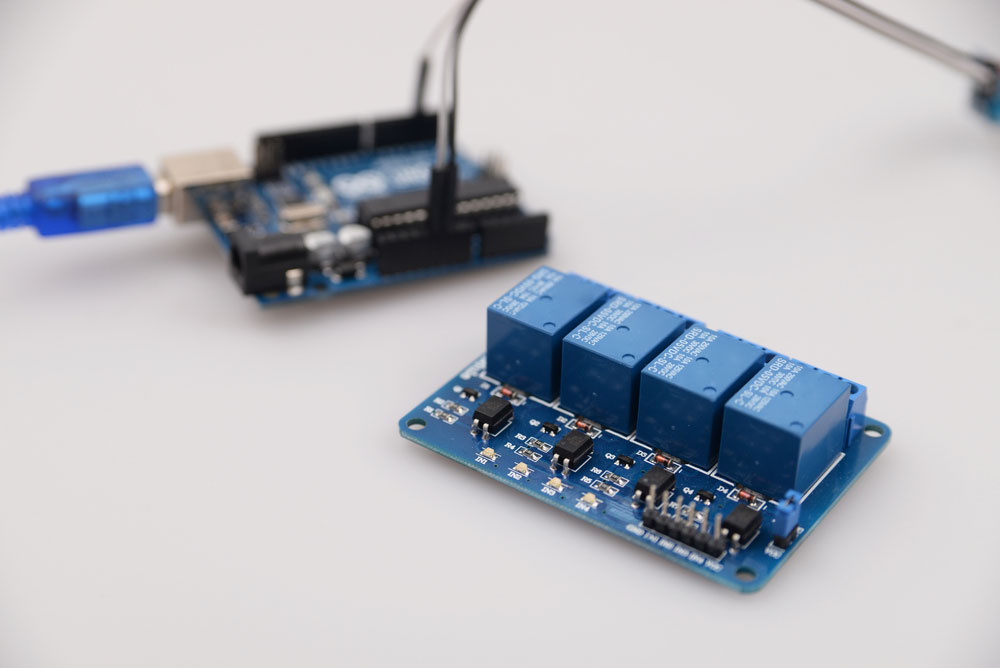
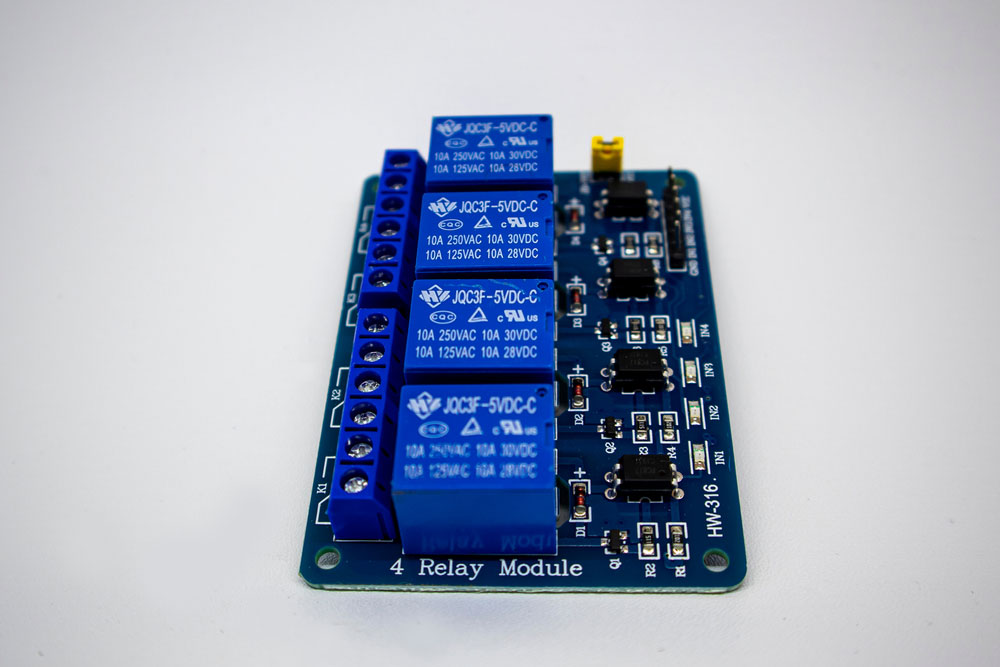 Four-channel relay module on white background
Four-channel relay module on white background
Firstly, we need to distinguish between relay and relay modules. A relay module is an array of one or more relays. While it is possible to purchase individual relays separate from the module, we recommend that you purchase them in a module format. This is because it comes with a few advantages.
On the input side of your standard single-channel relay module, you will find that you can access the relay’s input through three jumper pin connectors. You’ll find that the output connectors are wires suitable for a hardware connection. This makes it easier to attach whatever your single digital output load is. Most modules also have an LED at the bottom of the module. It turns on when you activate the relay and off when you deactivate it.
Additionally, there is a diode that goes across the electromagnetic coil that’s inside the relay. Essentially, it is what is known as a flyback diode. When we energize the coil and the relay reaches deactivation, it needs to discharge that count somewhere. This flyback diode prevents input voltage from going back into the output pin.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
Relay Module Applications
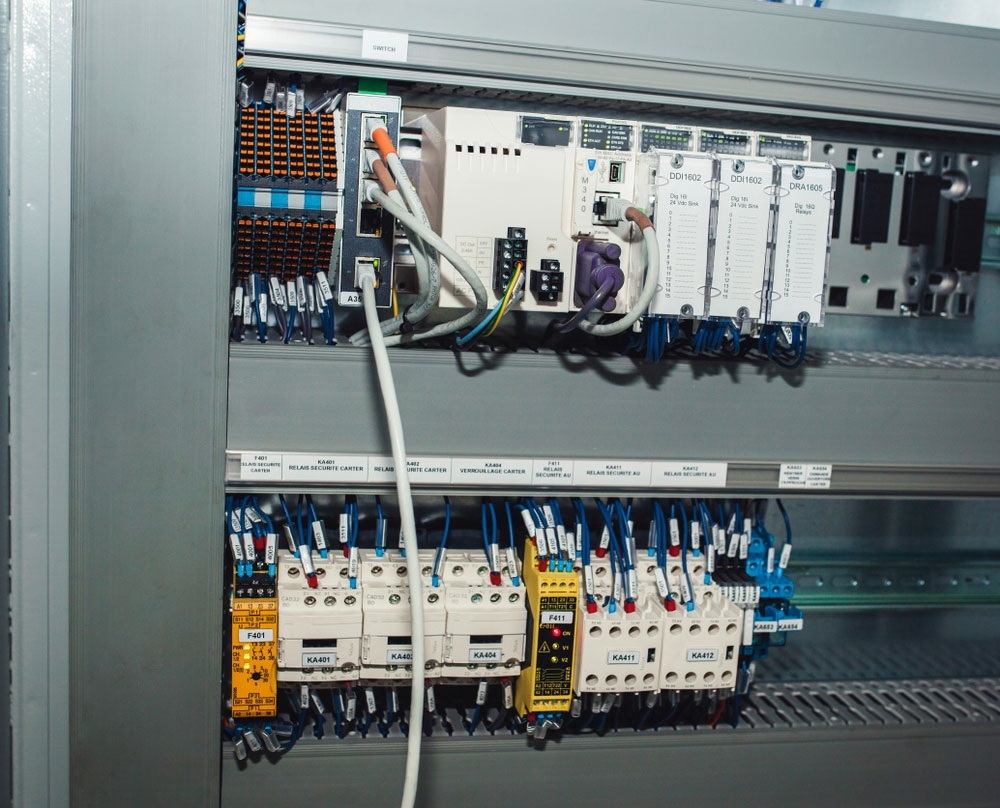

Relays, circuit-breakers, motor protections, and controllers extension modules
You can use your relay module in the following applications:
- Mains Switching
- Automating electrical appliances and lights in your home
- Isolated power delivery
- High Current switching
Arduino Relay Module
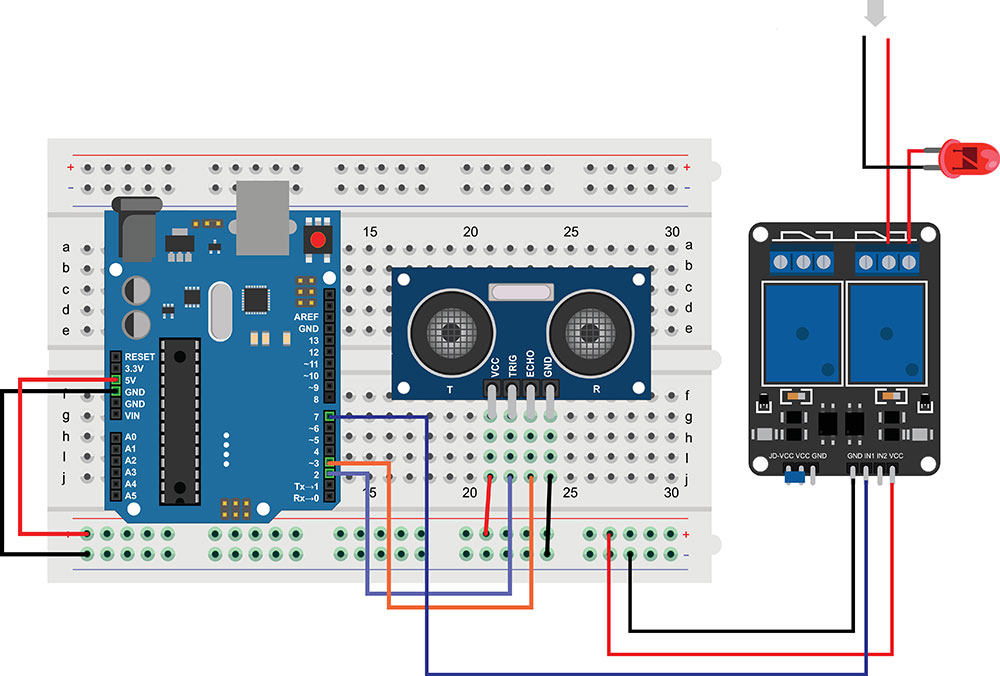
We have explored a few of the applications where you can use plain relay modules. The best way to integrate a relay module into your project is with a microcontroller such as an Arduino circuit board or Raspberry Pi. For instance, you can use your Arduino microcontroller and a relay module, and breadboard to create a motion sensor lamp.
Other Arduino projects include:
- Smartwatch Car Remotes
- Touchless Doorbells
- Alexa Smart Socket
- An ethernet powered home server
- Network Door Controllers
- Motion Detectors
- Power Adapters
*Note: To effectively pursue the above projects, you'll need additional software tools from Arduino.
Relay Module Circuit
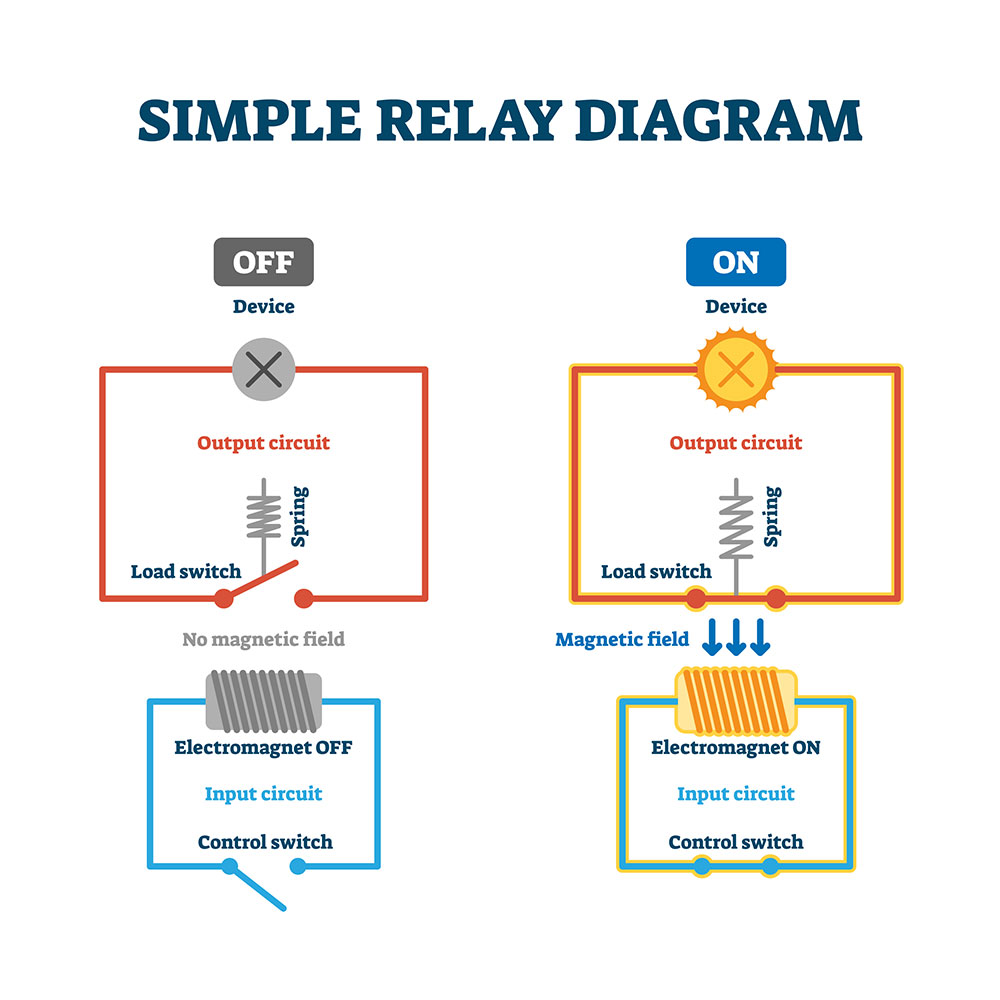 Simple relay diagrams
Simple relay diagrams
Markings on the relay module usually serve as an illustration for the inner circuitry. What you need to know most about a relay is the voltage and current it needs on the input side. Additionally, you will need to know the voltage that the relay can accept on the digital output side.
When we discuss 5V relays, we refer to the input it requires to energize the electromagnetic coil. For instance, your relay may have a number at the bottom that reads SRD-05VDC-SL-C. Essentially, this indicates that it is a 5-volt relay. Accordingly, it can control either an AC circuit at ten amps or a DC circuit at 30-volts and ten amps.
Types of Relay Modules
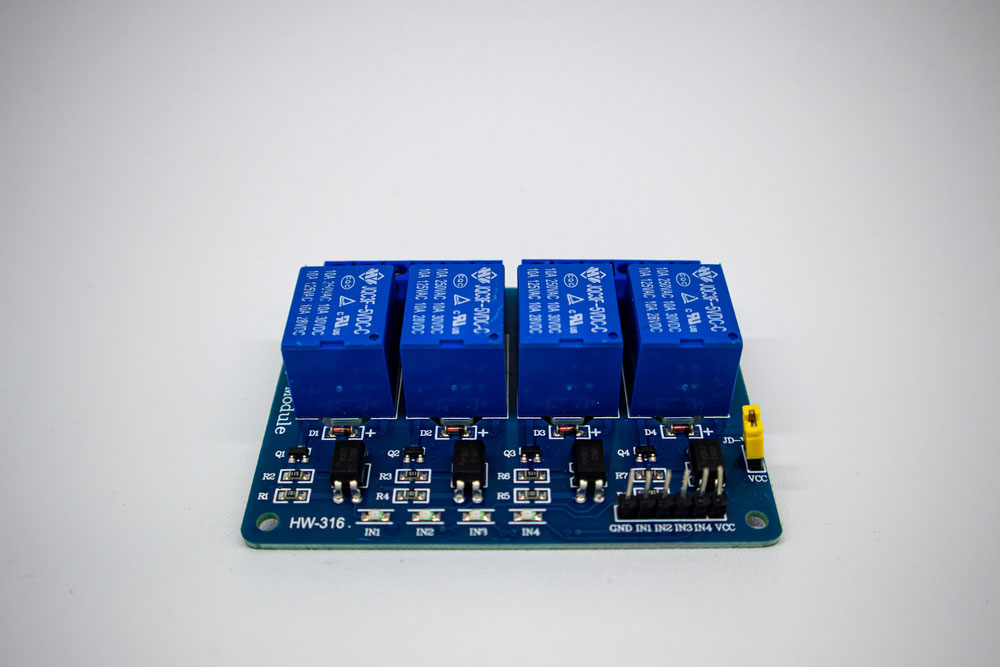 Horizontal relay 4-channel relay module
Horizontal relay 4-channel relay module
You can generally find a relay as either an electromechanical relay or a solid-state relay. Furthermore, electromechanical relays are the most common. The types of relay modules you are most likely to encounter include:
Types of Electromechanical Relays
- General Purpose Relays
- Reed Relays
- Machine Control Relays
Types of Solid-State Relays
- Zero-Switching Relays
- Instant On Relays
- Peak Switching Relays
- Analog Switching Relays
Channel Types
- Single/One Channel Relays
- 2-Channel SPDT Relay/Dual-Channel Relay Module
- 4-Channel SPDT Relay/Four-Channel Relay
- 8-Channel Relay Module
Conclusion
The above text should serve as a concise but detailed guide on relays. By the end of it, you should have a basic understanding of how to relay modules work and what options you have at your disposal. Regardless, we hope you have enjoyed reading this article. Thank you for reading.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!