Electrical components can be hazardous if they become too hot or are left exposed. So it is essential to use insulators to contain the heat or keep the current flowing without draining to unwanted areas. Circuit boards also have insulators to prevent short-circuiting and manage heat levels. We will look at the various types of PCB insulation and how their properties make them suitable for specific applications. Let's get right into it!
Contents
- What is PCB Insulation
- Importance of PCB Insulation Between Layers
- Creepage vs. Clearance
- PCB Insulation Materials
- FR-2
- FR-4
- RF
- Flex
- Metal
- How PCB Insulation Aids in Circuit Board Design and Operation
- Signal Layers and Insulation Thickness
- Board Type
- Board Elevation
- Thermal Progression
- What is PCB Insulation Coating
- PCB Insulation Coating Materials
- Conclusion
What is PCB Insulation
A PCB insulation or substrate is a non-conductive material that separates the copper traces in a printed circuit board. Insulation also restricts heat from warming up the entire board but dissipates it quickly to the air to protect against potential fires.
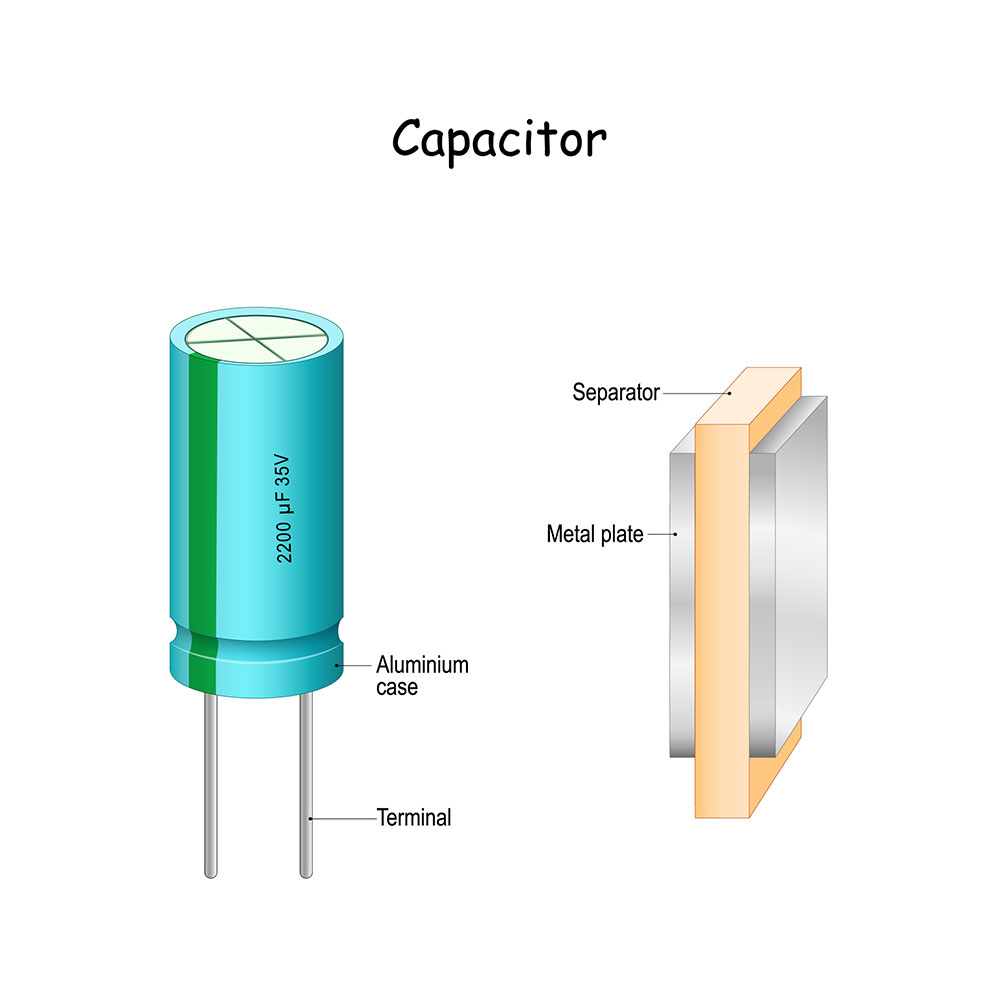
A separator or insulator in a capacitor. The same separation principle applies between PCB layers.
Importance of PCB Insulation Between Layers
Simple circuit boards can have single circuit layers, but the complex type can have over 20. The latter setup places multiple conducting layers close to each other, creating the possibility of interference. PCB insulation layers are responsible for separating these adjacent layers while ensuring the PCB remains as slim as possible.
Creepage vs. Clearance
Creepage is the shortest distance between two signal layers or conductive materials in a PCB when separated by the substrate. On the other hand, clearance is the shortest distance between two conductive traces separated by air. Understanding these two factors is essential for calculating the PCB insulation thickness and determining the best material for the application.
For instance, cheap toys can have low-quality insulation materials with short creepage and clearance distances. On the other hand, satellite PCBs require high-quality substrate materials with the minimum creepage distance being a little bit longer than the one in the toy.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
PCB Insulation Materials
The five typical PCB insulation materials include the following.
FR-2
FR-2 is one of the lowest-grade laminate substrates for PCBs. The flame-resistant insulator is a composite plasticized phenol resin and paper material. This composition makes it durable, lightweight, and easy to punch & mill. The material is also non-hydrophobic & halogen-free and is typical in single-sided PCBs and single-use consumer electronics.
FR-4
FR-4 is also a composite material consisting of woven fiberglass. But the high-grade, flame-resistant, dielectric material can withstand more physical pressure and higher temperatures than FR-2 substrates. Therefore, it is the ideal dielectric for multilayer and double-sided PCBs.
A PCB with green FR-4 substrate layers
FR-4 is arguably the most popular PCB dielectric because, despite having these impressive features, it is an affordable material. Therefore, most manufacturers use it to make high-end electronic devices. However, mechanically processing the material is not easy because you need tungsten carbide tools to machine, mill, and punch the board.
RF
RF is an acronym for Radio Frequency, so these substrates are ideal for applications requiring high-power microwaves or radio frequencies. And they are typical in military and aerospace applications.
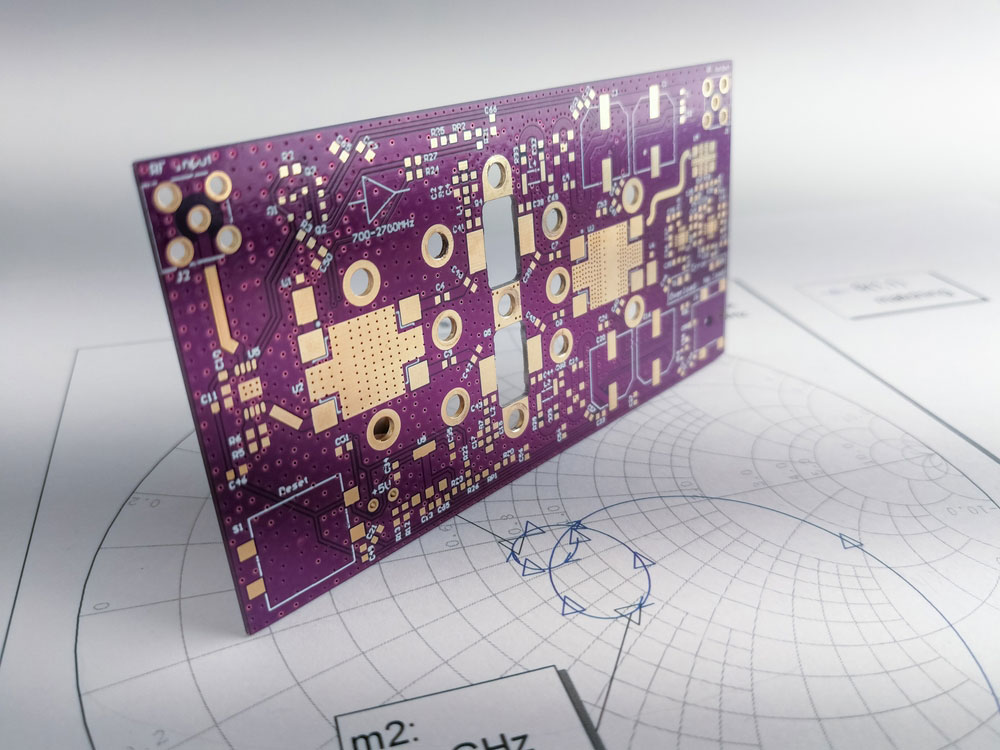
A high-power RF circuit board
The plastics used to make these substrates do not provide the best mechanical properties but have superb electrical performance. Therefore, boards with this insulator usually have one or two layers.
Flex
As the name suggests, flex circuit PCBs can bend in any direction without breaking. They require a similar insulation material that cannot snap when bent.

A flexible circuit board
These materials include plastic films and insulation sprays. Although thin and flexible, these substrates must be sturdy enough to hold the electronic circuit together.
Metal
Metal as an insulator sounds rather unconventional because the material is a conductor. But insulators have several functions, one of them being heat dissipation.
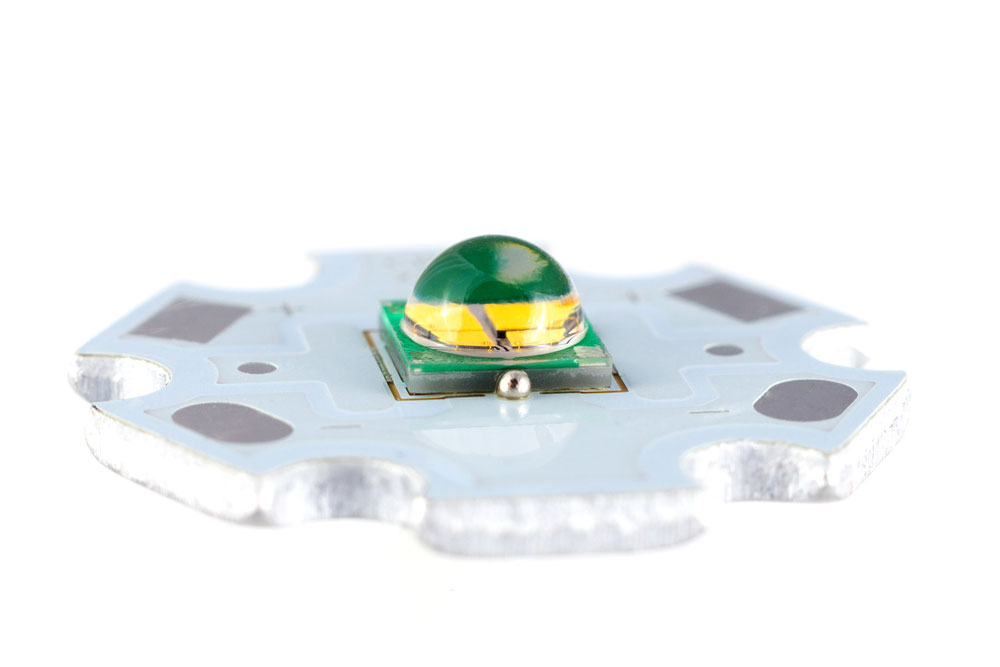

A high-power SMD LED on an aluminum PCB
Metal is a superb thermal conductor. So it is ideal for PCBs that handle high electrical currents because it ensures the high-powered devices don't break or burn.
How PCB Insulation Aids in Circuit Board Design and Operation
Circuit boards have evolved to have several complexities, such as multiple layers and signal routing. So you must pick the proper insulation, and here's how these materials help manage PCB operations.
Signal Layers and Insulation Thickness
Thin insulations between a ground and signal layer create detachments or isolations between the signals, which decreases the EMI issue. You can also use thicker dielectric between signal layers, but the conductive traces on one layer should run perpendicularly to the copper wiring on the adjacent layer.
Board Type
FR-4 is good enough for most boards. However, this insulation type is not ideal for high-speed or high-frequency boards because of the importance of controlled impedance. In such cases, the insulation material must meet the required impedance requirements and have the recommended height (thickness).
Board Elevation
Multilayer boards are typical in most industrial and commercial applications due to their compact size. But with more layers, the PCB will need more insulation layers to separate the PCB traces.
PCB traces on a circuit board
Since these boards cannot exceed a certain overall board height, you will have to coordinate the insulation height & type and the number of layers to fabricate and attain the required thickness.
Thermal Progression
A board gets exposed to high temperatures several times during manufacturing. Flex boards, for instance, go through more high-temperature cycles than their rigid counterparts. Therefore, they require materials with high heat dielectric properties.
What is PCB Insulation Coating
Insulation coating is the resistant material application on the PCB's outer layer surfaces. It can be through dipping, brushing, or spraying.
A PCB fresh from the fabrication process should meet the expected performance standards. But factors such as dust, corrosion, temperature, accidental impacts, mechanical stress, and harsh operating environments can affect its efficiency.
PCB insulation coating helps keep these factors at bay while enhancing a higher current incline and stopping electrical discharge. These benefits enable manufacturers to match the customer's integrity and compactness demands.
PCB Insulation Coating Materials
PCB insulation coating materials fall into the following five categories.
Polyurethane
Polyurethane coats are sensitive to humidity, stiff & solid, and difficult to take off. But they are resistant to solubles & acids, highly durable, and defy mugginess, which gives them several applications.

Paint adhesion coating testing on a PCB
However, the material's solid characteristic has some unfavorable effects. For instance, undoing defects on a polyurethane-coated board is challenging.
Besides that, the material's curing process takes time, during which its outer layer color can change to yellow when exposed to high temperatures. And it can damage screws.
Epoxy Resin
This protective coating is highly resistant to corrosion, temperature, and moisture. Additionally, it has superb permanency strength. These properties make it the most typical coating applied on circuit boards.
However, epoxy resin has its downsides. For instance, it shrinks and does not perform well in cold environments. Also, altering circuit boards coated with the material is challenging unless you strip it first. And stripping can stress the components mechanically, leading to damage.
Organic Silicon
Organic silicon is pliable and has high resistance to heat and moisture. So it is ideal for high-current PCBs because they have multiple dominant resistors that can be hot.
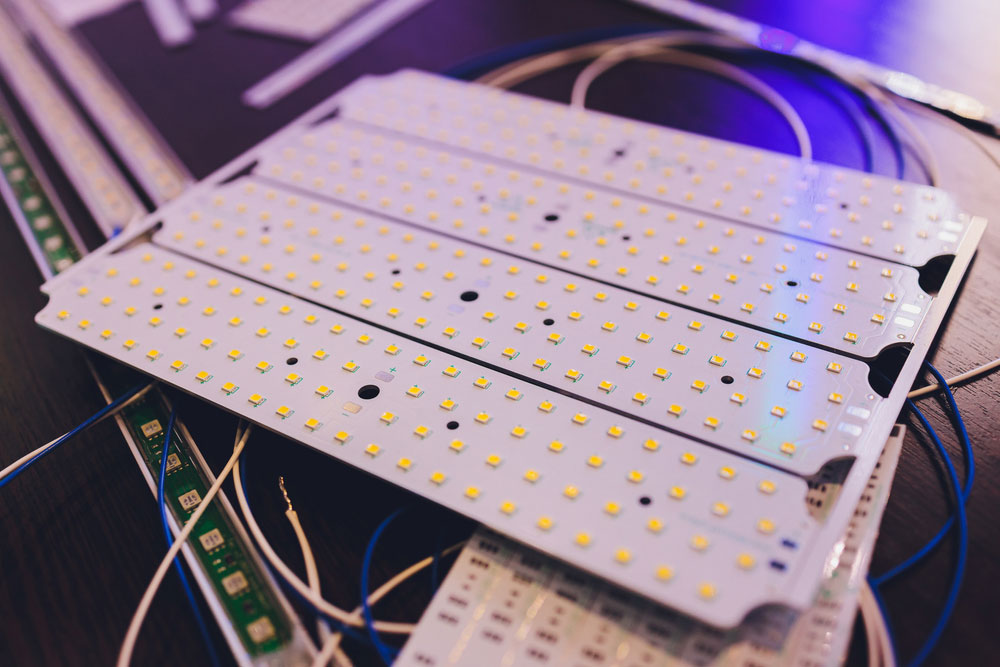
Silicone coating on an aluminum PCB for LED strip lights
But silicon is poor at resisting corrosion and maintaining mechanical stability, despite the material's remnants being tough to detach.
Parylene
This protective coating provides the best protection for high-frequency PCBs and offers the most efficient performance for highly compatible devices. It breaks the organic compound in vacuum valves, laying a sturdy even coat that provides thin coverage across the entire PCB surface. The only downside is that Parylene is expensive.
Acrylic Acid Resin
The acrylic acid resin type of PCB coating is most suitable for electronic devices because it is cheap and altering the coat is simple. On top of that, the material is flexible, adapts to dense circuits easily, dries quickly after application, and provides solid moisture resistance. Modifying circuit boards with this insulation coat is simple technologically because it depends on soluble evaporation.
Conclusion
There you have it! As much as conductivity is crucial in circuit boards, insulation is equally vital in ensuring proper functioning. And there are specific materials used for internal insulation between the layers and others for exterior coating. Each has its benefits and drawbacks, as shown above. We hope this article has been insightful and will help you pick the best insulation for your PCB. Better yet, you can contact us to build and assemble the most suitable PCBs for your project.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!