Contents
- What are the types of aluminum PCBs?
- What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Aluminum PCBs?
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Manufacturing Process of Aluminum PCBs
- Why use Aluminum PCBs?
- The Basic Structure of Aluminum PCBs
- 1. Circuit copper layer
- 2. Insulating/ Dielectric layer
- 3. Aluminum substrate
- What are the performance aspects of aluminum PCBs?
- Thermal Dissipation
- Thermal expansion performance
- Other performance introduction
- Typical application areas of aluminum PCBs
- Comparison with Other PCB Types
- Difficulties and solutions encountered in the production of aluminum PCBs.
- Copper etching
- Solder mask printing
- Machine-made
- How to Store Aluminum PCBs
- Partner with OurPCB for Your Aluminum PCB Needs
What are the types of aluminum PCBs?
| PCB Type | Description | Example Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Sided Aluminum PCBs |
|
|
| Double-Sided Aluminum PCBs |
|
|
| Multi-Layer Aluminum PCBs |
|
|
| Flexible Aluminum PCBs |
|
|

(a close-up of an IMS PCB)
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Aluminum PCBs?
Advantages
- Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum has a much higher thermal conductivity (237 W/mK) compared to FR4 (0.3 W/mK), allowing for efficient heat dissipation and improved thermal management.
- Durability and Lifespan: Aluminum PCBs are more durable and have a longer lifespan compared to traditional FR4 PCBs, making them suitable for applications with high-stress or harsh environmental conditions.
- Lightweight: Aluminum is a lightweight material, which is advantageous in applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in aerospace, automotive, and portable electronics.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Aluminum PCBs can be more cost-effective than copper-based PCBs, particularly in high-volume production, due to the lower material cost of aluminum.
- Environmental Friendliness: Aluminum PCBs are environmentally friendly, as aluminum is a recyclable material, and the manufacturing process is generally less harmful to the environment compared to traditional PCB production.
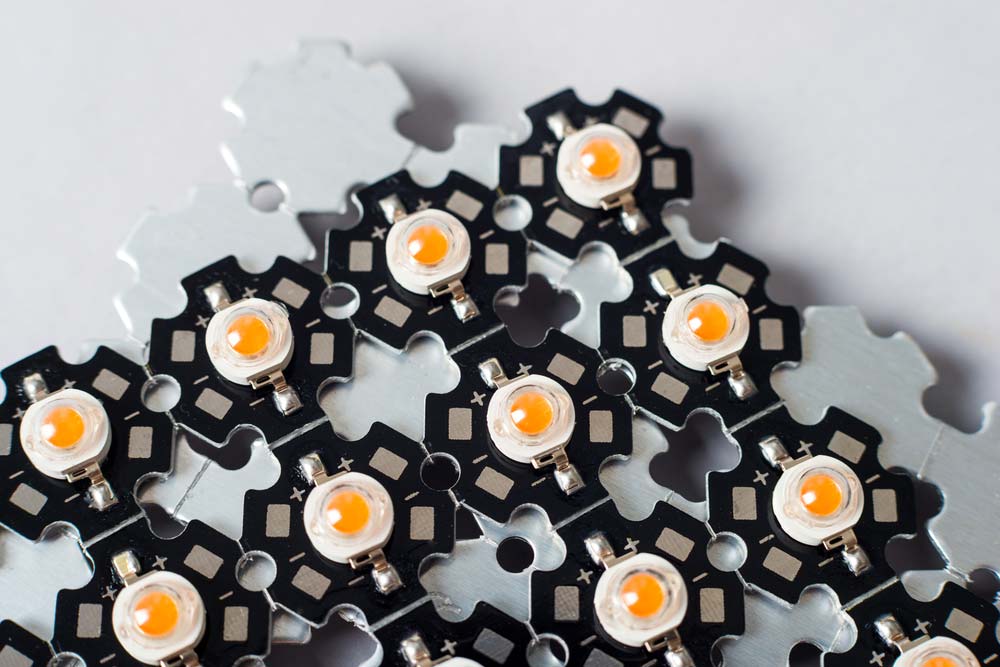

LEDs assembled on an aluminum PCB
Disadvantages
- Design Limitations: The material properties of aluminum can impose certain design limitations compared to FR4 PCBs, such as in terms of minimum trace widths and spacing.
- Higher Manufacturing Costs: The specialized manufacturing process for aluminum PCBs can result in higher costs compared to standard FR4 PCBs, especially for lower volume production.
- Moisture Sensitivity: Aluminum PCBs may be more sensitive to moisture and humidity compared to some other PCB materials, which can impact their performance in certain environments.
- Thermal Expansion Mismatch: The coefficient of thermal expansion for aluminum is different from that of the copper layers and other components, which can lead to reliability issues if not properly addressed in the design.
- Limited Availability of Suppliers: The number of suppliers and manufacturers of aluminum PCBs is more limited compared to the broader PCB industry, which can impact availability and lead times.
Manufacturing Process of Aluminum PCBs
The manufacturing process of aluminum PCBs typically involves the following steps:
-
Preparing the Aluminum Laminates: The aluminum substrate is coated with a thin dielectric layer, which serves as the insulation between the aluminum and the copper layers.
-
Generating the Circuits on the Copper Layer: The copper foil is etched to create the desired circuit patterns on the aluminum substrate.
-
Drilling Positioning Holes: Holes are drilled through the PCB to accommodate component placement and interconnections.
-
Solder Mask Printing: A solder mask is applied to protect the copper traces and prevent solder bridges.
-
Silkscreen Printing: Silkscreen printing is used to add component identification and other markings on the PCB surface.
-
Surface Finish Application: Various surface finishes, such as HASL, ENIG, or OSP, are applied to protect the copper traces and facilitate soldering.
-
Punching and Routing: The PCB is punched or routed to the desired shape and size.
Why use Aluminum PCBs?
Aluminum is the most common material due to its lightweight, cost-effectiveness, and ability to manage heat, making these PCBs ideal for applications like LED lighting, automotive systems, and power supplies where heat management is critical. Aluminum PCBs are also durable, lightweight, and cost-effective, making them a preferred choice in industries requiring efficient thermal performance.

(Technician repairing pcb layout with soldering iron)
The Basic Structure of Aluminum PCBs
Aluminum PCBs, also known as Insulated Metal Substrates (IMS), consist of several distinct layers, each serving a specific function. Understanding these layers is crucial for grasping how aluminum PCBs manage heat and provide electrical insulation. Below is a detailed breakdown of the basic structure of aluminum PCBs:
1. Circuit copper layer
This layer comprises an electrolytic copper foil ranging from 1 to 10 ounces (oz).
During its manufacture, the designer etches the copper material to form a printed circuit.
Its function is to apprehend the assembly and connect devices for ease of functionality.
It being an IMS, the substrate layer carries a higher current. Nonetheless, it still possesses a similar thickness and width to an FR-4 stiffener.
2. Insulating/ Dielectric layer
The dielectric layer is best known for its thermal conduction. In thickness, manufacturers estimate them to be approximately 50µm to 200µm thick. It can insulate, bond, and dissipate heat from the board during current flow.t
3. Aluminum substrate
The Aluminum Substrate is a key component in aluminum PCBs, providing mechanical support and effective thermal management. Made of lightweight and thermally conductive aluminum, it varies in thickness based on design needs.
The substrate enhances PCB durability, resists corrosion, and ensures structural integrity, making it suitable for demanding applications. Its high thermal conductivity aids in heat dissipation, preventing component overheating and enhancing reliability.
Aluminum substrates are commonly used in LED lighting, power electronics, and automotive/aerospace industries. Thermal vias and multi-layer designs further optimize heat management and circuit complexity.
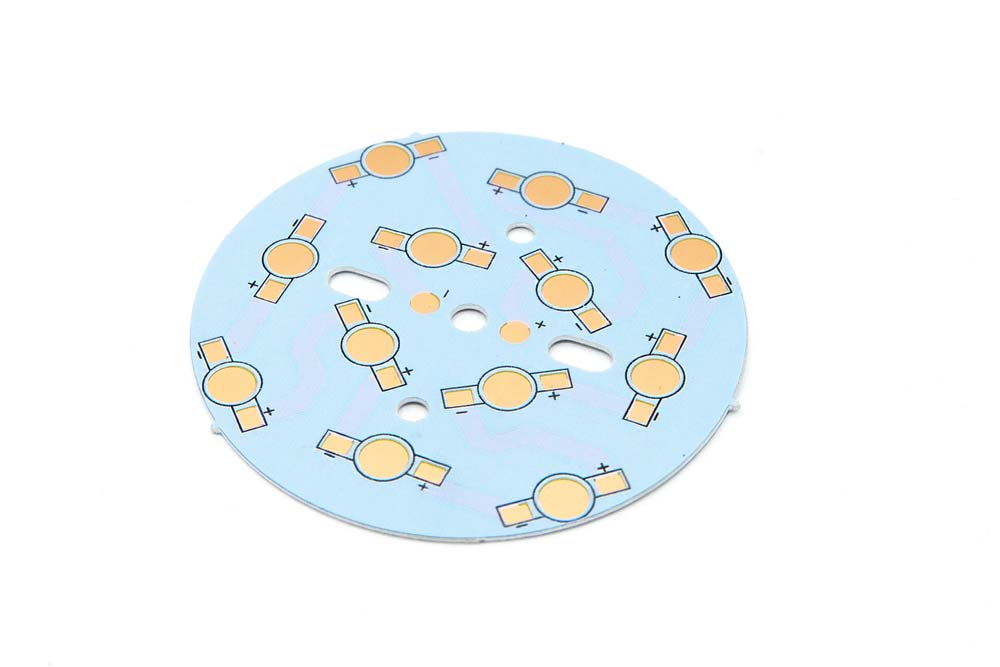
An aluminum PCB substrate
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
What are the performance aspects of aluminum PCBs?
Thermal Dissipation
There are the FR4 and CEM3, and then the aluminum substrate. The former are known as poor conductors of high thermal temperatures.
Higher temperatures can lead to an overall electrical components failure in the PCB, should you stick to the FR4 and CEM3.
An aluminum substrate works to curb the damage that may be brought about by heat dissipation.
Thermal expansion performance
You need to solve the dissipation challenge and thermal expansion and contraction, especially in the expansion problem of surface mount technology (SMT) expansion problem.
Regarding that, components on the board with different materials will have an improved life shell and stay reliable for extended periods
Dimensional stability performance
An aluminum substrate is more stable than the insulating substrate in the PCB.
For instance, if you heat the board from 30° C to 140 - 150° C, the aluminum substrate’s dimensional change will range from 2.5 to 3.0%
Other performance introduction
In addition to the three main performance aspects of an aluminum-clad PCB, using an aluminum substrate, PCB alternates with a brittle ceramic substrate for better protection.
Furthermore, the substrate advances the board’s heat resistance and physical properties, reducing the workload and manufacturing costs.
Typical application areas of aluminum PCBs
Aluminum PCBs apply to various technological equipment. They include but not limited to;
- Audio equipment: For instance, input and output amplifiers and power amplifiers.
- Power supply equipment, such as DV/AC converters and switching regulators.
- Communication electronic equipment
- Power modules, e.g., bridges, solid-state relays, converters, and power rectifiers.
- Office automation equipment
(a close-up of a motherboard)
Comparison with Other PCB Types
Compared to traditional FR4 PCBs, aluminum PCBs offer superior thermal management capabilities, making them the preferred choice for high-power and high-heat applications. However, aluminum PCBs may have higher manufacturing costs and design limitations due to their material properties.
Difficulties and solutions encountered in the production of aluminum PCBs.
Copper etching
Ideally, the copper foil you use in the circuit layer should be thick. A higher standard than this, which is more than 3oz, will force you to compensate for the etching’s width requirement.
Failure to do so will make the width intolerant to the etching. Therefore, you need to control the etching factors carefully, compensation being a major one.
Solder mask printing
A thick copper foil in this PCB design hinders solder mask printing of aluminum PCBs.
In other words, a thick layered trace copper makes the etched image have a vast difference in the trace surface and baseboard. Thus, printing becomes difficult.
Quickly solving this problem is using a quality solder mask oil. Alternatively, you can fill in the resin before the solder mask.
Machine-made
Manufacturing an IMS involves drilling mechanically, molding, and v-scoring, among others, centered on the internal via or holes.
To combat this, use the electric milling and professional milling cutter for manufacturing products of a lower volume.
Additionally, adjust the drilling parameters to stop burr production.
How to Store Aluminum PCBs
MCPCBs have a downside of attracting moisture, coloring yellow, or becoming black. Consider doing so within 48 hours after you’ve opened the vacuum package if you are to use it.
Store it in a dark and moist-free environment if it stays longer without usage.
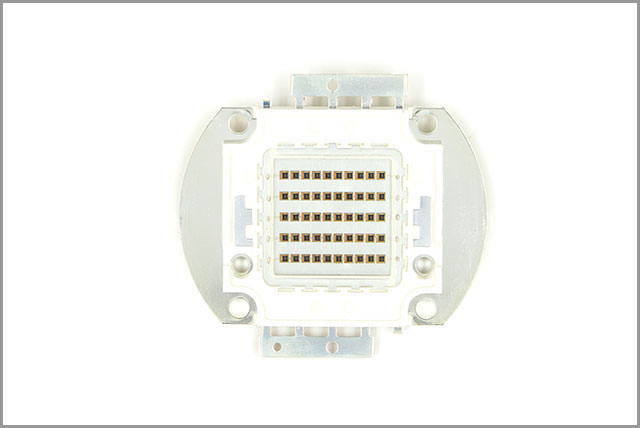

(aluminum Pcb on LED)
Partner with OurPCB for Your Aluminum PCB Needs
If you're looking for a reliable and experienced partner for your aluminum PCB manufacturing needs, look no further than OurPCB. Contact us today to learn more about our comprehensive solutions and how we can help you achieve your goals.
Back to Top: Aluminum PCBs
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!