Contents
- Types of 12V Power Supplies
- AC-DC vs. DC-DC Converters
- Constant Voltage vs. Constant Current
- Regulated vs. Unregulated Power Supplies
- Enclosure Types
- How does a 12V Power Supply Function?
- Basic Components
- How It Works
- Popular 12V Power Supply Models
- Applications of 12V Power Supplies in Various Sectors
- Role of 12V Power Supplies in PCB Functionality
- Powering Components
- Voltage Regulation
- Noise Reduction
- Heat Management
- Compatibility with Battery Systems
- How to Choose the Right 12V Power Supply
- Power Requirements of Device
- Compatibility with Devices
- Durability and Reliability
- Safety Features
- Noise Levels
- What are Common Issues with 12V Power Supplies?
- Overheating
- Voltage Fluctuations
- Short-Circuiting
- Troubleshooting, a 12V Power Supply
- 1. Safety First
- 2. Visual Inspection
- 3. Check the Output Voltage
- 4. Load Testing
- 5. Inspect Internal Components
- 6. Test with a Functioning Power Supply
- 7. Ask a Professional
- Design Considerations for 12V Power Supplies in PCBs
- Optimize Layout and Placement
- Thermal Management Techniques
- Ensure Power Integrity
Types of 12V Power Supplies
AC-DC vs. DC-DC Converters
-
AC-DC Converters: These convert alternating current (AC) from a wall outlet to direct current (DC) suitable for electronic devices. Examples include the MEAN WELL RS-150-12, which is an AC/DC power supply delivering 12V DC.
-
DC-DC Converters: These convert one level of DC voltage to another, often used in automotive or portable applications where the primary source is already DC.
Constant Voltage vs. Constant Current
-
Constant Voltage: Maintains a steady voltage output regardless of the load, ideal for devices like LED strips and CCTV cameras.
-
Constant Current: Maintains a steady current output, suitable for applications like LED lighting where consistent brightness is required.
Regulated vs. Unregulated Power Supplies
-
Regulated Power Supplies: Provide a stable output voltage despite variations in input voltage or load conditions, enhancing the reliability of connected devices.
-
Unregulated Power Supplies: Output voltage can vary with changes in load and input voltage, typically used in less critical applications.
Enclosure Types
-
Open Frame: Exposed components, suitable for controlled environments.
-
Enclosed: Protected casing, ideal for general-purpose use.
-
Wall-Mounted: Designed to be mounted on walls, saving space and facilitating easy installation.
How does a 12V Power Supply Function?
Understanding how a 12V power supply works will help you understand how appliances work in more detail.
Basic Components
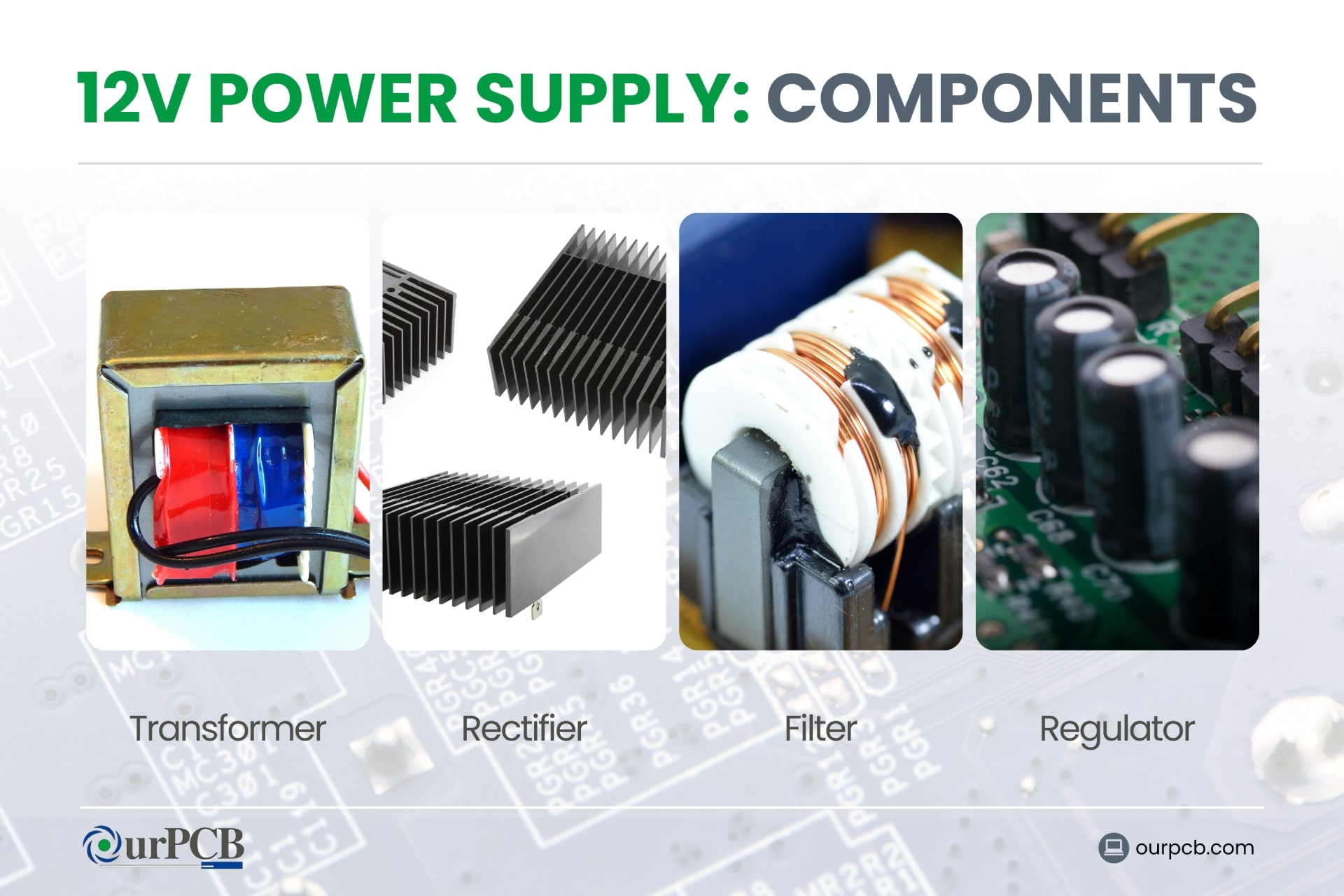
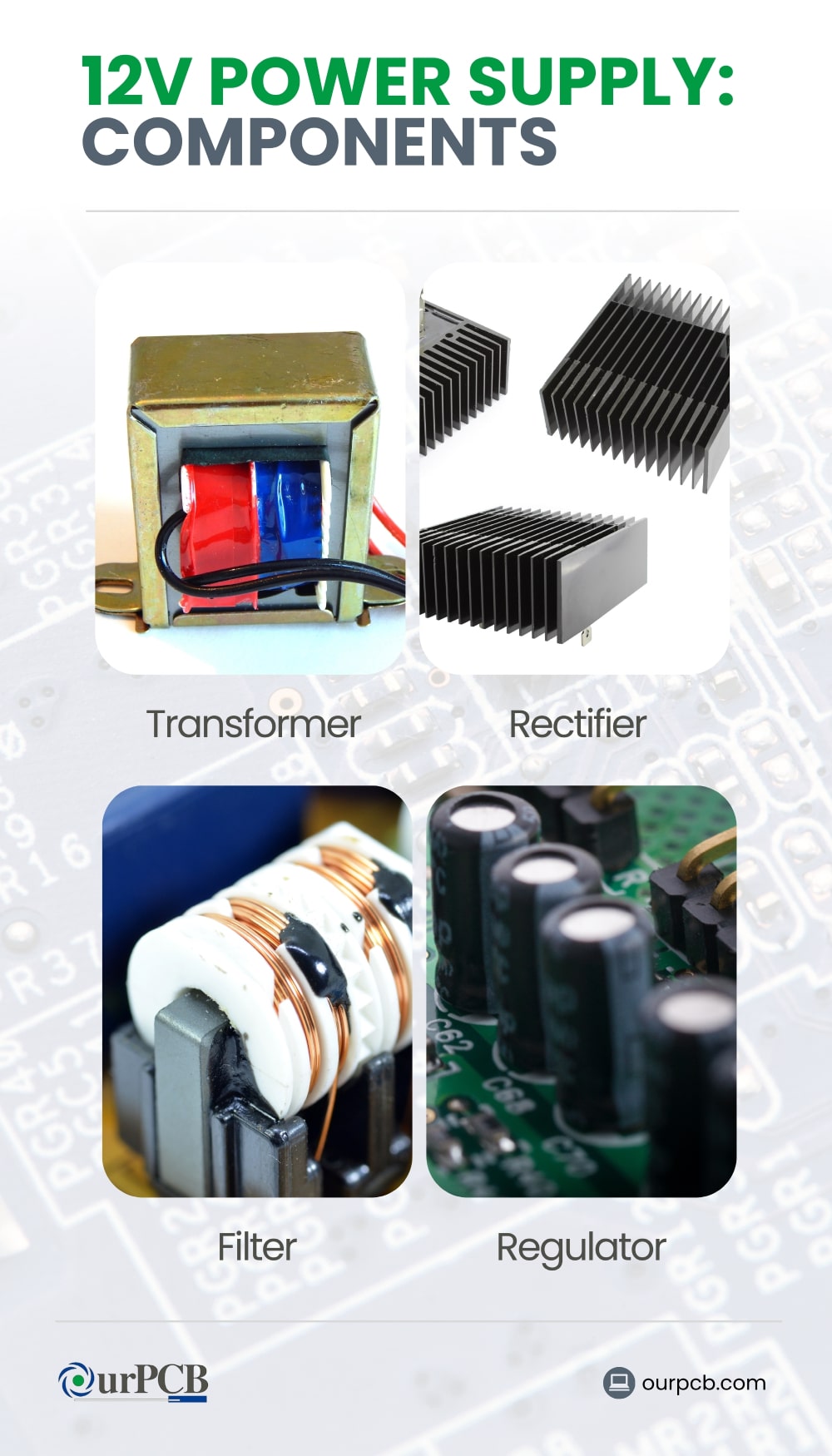
- Transformer: The transformer reduces the high voltage from the power source (like a wall outlet) to a lower voltage, for safety and efficiency.
- Rectifier: After the voltage is reduced, it goes through the rectifier, which converts the alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). Most electronic devices operate on DC, so this is an essential step.
- Filter: The filter smooths out the DC signal, removing any fluctuations or ripples for a steady and consistent voltage output.
- Regulator: The regulator keeps the output at a constant 12V, even if the input voltage or load changes.
How It Works
- Step-Down Voltage: When the power supply is plugged in, the transformer reduces the high AC voltage to a lower AC voltage, closer to what’s needed for the 12V output.
- AC to DC Conversion: The rectifier then converts this lower AC voltage into a pulsating DC voltage. This initial DC signal still contains some AC components, known as ripples.
- Smoothing the Signal: The filter smooths these ripples, producing a more stable DC voltage. However, this voltage can still vary slightly with load changes.
- Voltage Regulation: Finally, the regulator fine-tunes the DC output to a precise 12V, so it remains constant even if the input voltage fluctuates or the load varies.
Popular 12V Power Supply Models
| Model | Type | Output Voltage | Current | Power | Connector/Additional Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEAN WELL PM-20-12 | Medical, Single Output | 12V DC | 1.8A | 22W | - |
| MEAN WELL RS-25-12 | - | 12V DC | - | 25W | - |
| MEAN WELL RS-150-12 | AC/DC Power Supply | 12V DC | - | - | - |
| GESD 12V Power Supply | Universal, Regulated | 12V DC | 10A | - | - |
| IRM-60-12ST MEAN WELL | AC/DC Power Supply | 12V DC | - | 60W | - |
| MEAN WELL RS-50-12 | - | 12V DC | - | 50W | - |
| Compact 12V DC Adapter | - | 12V DC | 300mA | - | Connector Size: 5.5x2.1mm, Input: 100-240V AC |
| Delta 12V Power Adapter | - | 12V DC | 2A | - | With Plug, Indoor |
| The Antenna Farm | - | 13.8V DC | 9A | - | Battery Backup: Yes |
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
Applications of 12V Power Supplies in Various Sectors
Selecting the right power supply is crucial for the reliable and efficient operation of numerous devices and systems across different industries. Below is a detailed table outlining the applications of power supplies in consumer electronics, industrial settings, and distinguishing between outdoor and indoor uses.
| Category | Application | Description | Example Products |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | LED Lights | Provide consistent power for indoor and outdoor lighting solutions, ensuring energy efficiency and long-lasting illumination. | Delta 12V LED Power Adapter |
| Security Cameras | Ensure reliable operation of surveillance systems by delivering stable and uninterrupted power, critical for security monitoring. | MEAN WELL PM-20-12 UL/cUL Approved Power Supply | |
| Audio Equipment | Power various components in home and professional audio setups, maintaining high-quality sound and performance. | Compact Enclosed Adapters for Audio Systems | |
| Industrial Applications | Machinery Control Systems | Deliver stable power for automated equipment, ensuring precision and reliability in manufacturing and production processes. | Durable Industrial-Grade Power Adapters |
| Medical Devices | Require precise and reliable power sources to meet stringent industry standards and ensure the safe operation of medical equipment. | MEAN WELL PM-20-12 UL/cUL Approved Power Supply | |
| Outdoor vs. Indoor Use | Outdoor Applications | Power supplies designed for durability and weather resistance, suitable for harsh environmental conditions often encountered in outdoor settings. | Delta 12V Power Adapter with Plug-In Connectors |
| Indoor Applications | Enclosed and compact adapters ideal for controlled environments with minimal exposure to harsh conditions, ensuring safety and efficiency indoors. | Compact Enclosed Adapters for Indoor Electronics |
Role of 12V Power Supplies in PCB Functionality
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the backbone of most electronic devices. A 12V power supply is commonly used due to its balance of power and efficiency. Here’s how it fits into PCB functionality.
Powering Components
One of the primary roles of a 12V power supply in a PCB is to provide the necessary voltage to power various components. Many electronic parts, like relays, motor, and some integrated circuits, require a stable 12V supply to operate correctly.
Voltage Regulation
PCBs often contain sensitive components that need a precise voltage level to function without damage. A regulated 12V power supply can provide stable voltage, preventing harmful fluctuations.
Noise Reduction
Electrical noise can negatively affect the performance of a PCB. A 12 volt power supply can help reduce electrical noise, giving you cleaner power delivery. This noise reduction is especially important in audio and video equipment, where noise can degrade signal quality.
Heat Management
Managing heat is vital in any electronic device. A 12V power supply typically generates less heat compared to higher voltage supplies, which makes it easier to manage thermal conditions on the PCB.
Compatibility with Battery Systems
Many portable and backup power systems use 12V batteries. Using a 12V power supply in a PCB design ensures compatibility with these battery systems. This simplifies the design process for devices that can switch seamlessly between mains power and battery power without needing complex voltage conversion circuits.
How to Choose the Right 12V Power Supply
When it comes to powering your PCBs, choosing the right 12V power supply can influence whether your devices stay safe or are at risk. Here are some key factors to consider.
Power Requirements of Device
Understanding the power requirements of your device is the first step in selecting the best 12V power supply. Look at the device’s wattage or current draw (measured in amps). The power supply should provide at least as much current as the device requires.
Compatibility with Devices
Make sure the power supply is compatible with your devices. Check the voltage and current ratings to match the specifications of the device you want to use it with. Some devices may have specific power requirements, so always read the manufacturer’s recommendations first.
Durability and Reliability
Look for power supplies with good build quality, robust casing, and high-quality components. Brands with a reputation for reliability and positive user reviews are often a safer choice.
Safety Features
Safety should never be overlooked when choosing a power supply. Make sure the power supply has built-in safety features such as overvoltage protection (OVP), over-current protection, and short-circuit protection.
Certifications from recognized bodies like UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or CE (Conformité Européenne) indicate that the power supply meets safety standards. These features protect both the power supply and your devices from potential damage.
Noise Levels
Some power supplies have cooling fans that can generate noise. If noise is a concern, look for fanless models or those with quiet operation. Check user reviews for comments on noise levels to make sure you choose a power supply that won’t be disruptive in your setting.
What are Common Issues with 12V Power Supplies?
Knowing what to expect from 12V power supplies can help you avoid problems, while knowing that you can fix them will put your mind at ease in case you do experience issues.
Overheating
Overheating is a frequent problem with 12V power supplies. It can happen when the power supply operates outside its recommended temperature range or if the power supply needs to provide more power than it was designed to handle. Always ensure proper ventilation and use power supplies within their rated capacity can help prevent overheating.
Voltage Fluctuations
Voltage fluctuations might be due to input overvoltage or undervoltage, which can be caused by electromagnetic disturbances like power surges or sags. To mitigate this, many power supplies include features like overvoltage and undervoltage protection (UVP) to shut down the unit when voltage levels are unsafe.
Short-Circuiting
A short circuit happens when there’s an unintended path of low resistance, and an excessive amount of current flows through the circuit. This can lead to overheating and potentially even cause fires. Many power supplies are equipped with short-circuit protection, which shuts down the output if a short circuit is detected.
Troubleshooting, a 12V Power Supply
A 12V power supply is commonly used in various electronic devices and systems. When it malfunctions, it can disrupt the performance of the connected equipment. Here are some steps to help you troubleshoot a 12 volt adaptor.

1. Safety First
Before you begin troubleshooting, make sure you’re safe by following these steps:
- Turn off Power: Disconnect the power supply from the mains and any connected devices.
- Wear Protective Gear: Use insulated gloves and goggles to protect yourself against electric shocks.
- Work in a Safe Area: Make sure your workspace is dry and free from flammable materials.
2. Visual Inspection
Once the power is off and your device is disconnected, start with a thorough visual inspection of the power supply. Look for:
- Burn Marks or Smell: Signs of burnt components can indicate overheating or electrical failure.
- Loose Connections: Check for loose or disconnected wires, which can cause intermittent power issues.
- Damaged Components: Inspect for swollen capacitors, broken resistors, or other damaged parts.
3. Check the Output Voltage
Use a multimeter to measure the output voltage of the power supply.
- Set Multimeter: Turn the multimeter to the DC voltage setting.
- Measure Voltage: Place the multimeter probes on the output terminals of the power supply. A healthy 12V power supply should read close to 12 volts.
- Analyze Results: If the voltage is significantly lower or higher than 12V, then the power supply may be faulty.
4. Load Testing
Testing the power supply under load can help determine if it performs correctly under operational conditions.
- Use a Dummy Load: Connect a resistor or a test load that matches the power supply's rated output.
- Measure Voltage Under Load: Check if the voltage remains stable when the load is connected. Significant voltage drops can indicate issues with the power supply.
5. Inspect Internal Components
If the external checks don’t reveal any issues, you may need to open the power supply casing to inspect the internal components.
- Capacitors: Check for bulging or leaking capacitors.
- Transformers and Inductors: Look for signs of overheating or damage.
- Fuses and Diodes: Make sure fuses are intact and diodes are functioning correctly.
6. Test with a Functioning Power Supply
To rule out issues with the connected device, test it with a 12V power supply that you know is working correctly.
- Swap Power Supply: Connect the device to a functioning power supply.
- Check Operation: If the device works properly, the original power supply is likely to be faulty.
7. Ask a Professional
If you’re unable to identify or fix the issue yourself, it may be time to consult a professional.
- Warranty: Check if the power supply is still under warranty.
- Professional Repair: Contact a professional technician or the manufacturer for repair or replacement options.
Design Considerations for 12V Power Supplies in PCBs
Designing a 12V power supply for PCBs involves several key considerations. Here’s what to think about when designing PCBs. If you’re unsure, OurPCB can design your PCBs for you!
Optimize Layout and Placement
Place power supply components close together to minimize trace lengths and reduce resistance and inductance. This helps maintain a clean power supply and minimizes electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Also, use wider traces to handle higher currents and reduce heat buildup. Keep the input and output sections of the power supply separated to avoid unwanted coupling and interference.
Thermal Management Techniques
Use thermal vias and pads beneath heat-generating components to transport heat away quickly. Incorporating heat sinks, thermal vias, and copper planes can help dissipate heat effectively.
In high-power applications, consider using fans or other active cooling methods to maintain optimal operating temperatures. Proper thermal management in PCB design helps the power supply operate efficiently without overheating and ensures long-term reliability of electronic components.
Ensure Power Integrity
Power integrity is about maintaining a stable and clean power supply to all components on the PCB. Use decoupling and bypass capacitors to reduce noise and prevent voltage drops near components’ power pins.
These capacitors help mitigate ground bounce and ringing caused by rapid switching of integrated circuits (ICs). Implementing a solid ground plane can also provide a low impedance path for return currents and help in reducing EMI and crosstalk.
If you found this article on informative, you may be interested to learn about Hex Inverter - IC, Chip, Circuit, Logic, Breadboard Simulator - Virtual, Online, and Circuit Simulators.
Back to Top: 12V Power Supply | Power Supplies 12V, 12V DC Power Supply, 12VDC
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!