Before certifying a new batch of printed circuit boards (PCBs) as safe and of high quality, they need to pass specific tests. One of these tests is the "Electronics Environmental Testing." This testing involves passing the PCBs through various environmental tests, which are essential for PCB manufacturing. The purpose is to confirm their reliability under different ecological conditions. Only after successfully completing these tests can a PCB manufacturer ensure that their products meet the rigorous standards expected from PCB fabrication and assembly manufacturers.
So, are you a manufacturer or an engineer that plans to buy a batch of PCBs?
Then, you need to have an in-depth knowledge of this subject topic.
The good news is:
We've created this article to give you in-depth information about:
- Electronics Environmental testing
- Electronics testing
- Types of Testing required to certify PCBs
And many more.
So, if you're ready, let's the kick off.
Contents
- Introduction To Environmental Testing
- Electronics Environmental Tests: Types of Testing
- Vibration Testing
- Cycling and Thermal Shock
- Highly Accelerated Tests
- Burn-In Testing
- Humidity and Corrosion
- Other Key Environmental Tests
- Table of Environment and Equipment Class Based on a Few Test Procedures
- What Are the Categories of Electronics Environmental Testing?
- Parametric Testing
- Functional Testing
- The Bottom Line
Introduction To Environmental Testing

Environmental Testing Equipment
Source: Nara. get archive
So, what exactly is an environmental test of electronics?
Put:
It involves carrying out different environmental testing techniques to meet multiple environmental conditions.
Also, every test done must meet the environmental standards of the IEC 60068.
Why? The purpose of the test is to ensure that every PCB created by a manufacturer can survive and function appropriately under harsh and extreme conditions.
So, no matter the environmental factors, the product must have structural integrity and meet specific reliability requirements.
Here are a few examples of the type of testing that happens during the testing procedures:
- Electrical testing
- Vibration testing
- Reliability testing
- Altitude testing
- Life testing
And many more.
So, whether it's a thermal shock, vibration, electromagnetic interference test, the PCB must be able to withstand:
- Harsh conditionals
- Operational environment
Now that we've got a clear understanding of what environmental electronics tests involve let's jump into the type of tests.
Electronics Environmental Tests: Types of Testing
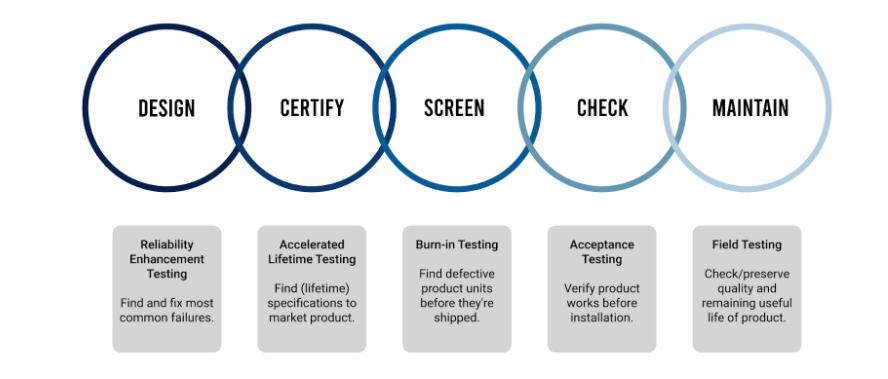
Electronics Reliability Test Diagram
Source: Wikimedia Commons
Vibration Testing

GPM vibration testing equipment
Source: Wikimedia Commons
This test procedure involves a product mimicking the likely conditions it may face—under a testing environment.
So, the test makes it possible to check how robust and safe a product can be during its operation. Also, you can monitor and check for performance bottlenecks and failures with this test—before certifying a product for use.
But that's not all.
An excellent vibration test procedure should be able to meet critical electronics standards globally like:
- IEEE and IEC procedures for electronic products
- RTCA DO-160 for automotive and aerospace products
- BS, ISO, ASTM standards for all products
Also, setting up vibration testing is usually more expensive than other test standards in this article. Plus, low amplitude/frequency vibration testing is usually the costliest.
Cycling and Thermal Shock
Thermal shock testing involves you altering the temperature of a PCB.
So, you perform this test to find out one thing:
How thermal contraction and expansion influence the sturdiness of the PCB board.
For this test, you'll have to fluctuate the board's temperature at two different extreme temperatures. Hence, you need a two-chamber system to run it—below 0o C and above 130 o C.
Thermal Shock Rig
Source: Picryl
But for thermal cycling, the testing involves only one chamber. Plus, you can change the temperature from one extreme range to another at 10 degrees centigrade per minute.
Highly Accelerated Tests
This test comprises of two different procedures:
HASS (Highly Accelerated Stress Screen)
HALT (Highly Accelerated Life Test)
So, both tests help to show the sturdiness of a product in specific controlled environments with:
- High humidity
- High temperature
- Shock or Vibration Tests
Also, it would help if you carried out these tests while your device was on.
So, what's the purpose of these tests?
Simple! The tests help to mimic the situations that could cause a new product to fail. So, to run the test, you've to keep the products in a simulated environment.
However, many product engineers are usually hesitant to undergo the HASS or HALT test for products.
The reason is simple! There's usually a ton of stress mounted on the products so that the procedure might become over-spec.
In simpler terms;
The stress on the tested products may surpass the normal conditions in a stable environment.
Hence, most engineers don't like to fix problems in products with HALT/HASS test compliance.
Burn-In Testing
The goal of the burn-in test is to find out failing components aboard. So, you've to employ extreme temperatures and voltages for an extended period. That way, you can detect any glitches before mass-producing the boards.
Also, this test helps you improve the design reliability of every board component. So, the testing process involves you applying a component failure rate per time—to create a bathtub curve.
So, if you want to find board component glitches early, the burn-in test is the go-to procedure—which takes about 48 – 168 hours.
Humidity and Corrosion
It's a common thing for you to see PCBs used in humid surroundings. So, it's not surprising that water absorption is a standard test to check for the sturdiness of a PCB.
Here's the thing;
This test involves you weighing a PCB and placing it in a space that has controlled humidity. So, if water enters the board, the weight of the board will increase. And any slight change in the importance of the board means the council has failed the humidity test.
As you carry out the tests for humidity, check if the exposed conductors corrode—which shouldn't happen in a humid surrounding. If it does, then the board has failed the corrosion test. That's why product engineers plate (with oxidation-resistant composite) exposed copper to avoid oxidation.
A few examples of oxidation-resistant components are:
- HALL
- Nickel-gold
- ENIG
- Nickel
- ENIPIG
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
Other Key Environmental Tests
Here are other environmental tests that you can use:
- Cryogenic Testing
- Altitude Cycling Test
- Merged Environmental Test
- Weathering
- Dust Protection Test
- Ingress Protection Certificate
- Electrical Stress Test
- Flammability Test
- Climatic Testing
- Condensation Test (Under Cyclic and Constant Climatic Environment)
- Temperature Humidity Bias Test (THB)
- Dry Heat Test (Endurance)
- Salt Spray Test
- Seismic Testing
- Low-Pressure Test
- Five-point margin Test
- Design and Development Testing
- Production Monitoring
- Cold (Operational)
- On-going reliability Test
- Standard Compliance Tests
- Laser Vibrometry Testing of Technical Products
- Dry Heat Test )Operational)
- Damp Heat, Steady State (Endurance)
- Transport Simulation
- Temperature Change (Operational)
- Wet Heat, Steady State (Operational)
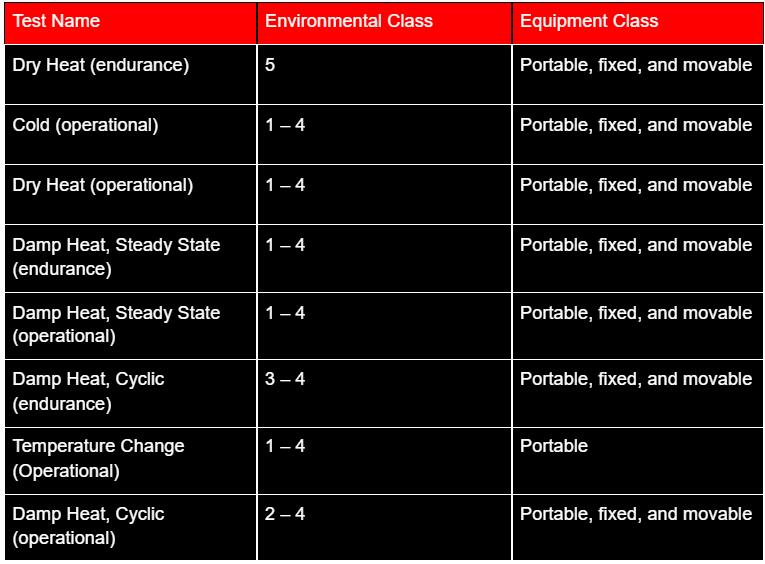
Table of Environment and Equipment Class Based on a Few Test Procedures
Here's a table showing equipment and environment-class of a few test procedures:
What Are the Categories of Electronics Environmental Testing?
There are two major categories of environmental testing;
Parametric Testing
This testing category involves you taking comprehensive scrutiny and checking the measured constraints of a product while undergoing a test.
So, with it, you can observe altering parameters as certain environmental conditions occur. Plus, it comes with a unique DV testing value.
Functional Testing
Functional testing is the most common environmental testing category that encompasses different stages of production and design.
If you want to get the best out of this testing category, ensure to run it consistently.
For instance, alterations in the temperature of a product can lead to "soft failures." And these soft failures could occur in a few "environmental conditions" and be absent at another.
So, the rule of thumb is to monitor the product to avoid such epileptic failures continuously.
But the "hard failures" appear at low-level performance analysis. No doubt, they have a shorter duration than "soft failures," but you can miss them easily.
The Bottom Line
As a product designer or engineer, you can't ignore the importance of environmental electronics testing. It would help if you had them to determine and certify products that are suitable for mass use.
Plus, you can't meet specific electronic IC standards if you don't run these tests. That's why it is essential to understand the two categories of these tests and the types of testing for different electronic devices.
Luckily, we've mentioned the categories and types of environmental tests in this article.
Also, you'll be glad to know that at ourpcb, we carry out specific environmental tests like:
- High and low-temperature tests
- Moisture resistance test
- Temperature impact test
- Steady humidity and heat test
- Salt spray test
- Solar radiation test
- Vibration test
- Impact response spectrum
- Environmental stress screening
And many more.
So, if you'd like to have the complete list of all the environmental tests we do, feel free to reach us.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!