Running a computer system requires computer memory. In the entire computer system, it's one of the vital components. Therefore, it's important that you have basic knowledge about computer memory and know the types available. This article will describe classifications of computer memories and compare primary memory with secondary memory. Let's get started!
Contents
- Types of Computer Memories
- Primary Memory
- Secondary Memory
- Primary Memory: ROM vs. RAM Comparison Chart
- Why Computer System Need Primary Memory
- Classification of Primary Memory
- Read-Only Memory
- Random Access Memory
- Types of Secondary Memory
- SSD: Solid-State Drive
- HDD: Hard Disk Drive
- Flash Drives
- NAS: Network-Attached Storage
- SAN: Storage Area Network
- Tertiary Memory: Cloud Storage
- Primary Memory Vs. Secondary Memory
Types of Computer Memories
Computer memories play an essential part in the specialized computer system. It stores instructions and data on computer systems to client computers and performs various tasks. Typically, it's an efficient storage space that fetches and stores data. The memory comprises large portions divided into small parts called location/cell. Each million memory cells have a distinctive size and index number.

Assorted digital storage devices
There are two types of computer memories;
Primary Memory
Primary memory is also referred to as the internal memory, and within the specialized computer system, it's the main memory. Since it's the internal memory, it accesses data faster, and it's the most volatile part of the computer. In case of a power single failure, data in primary storage devices won't exist if not saved.
Being semiconductor memories, the primary memory is more pricey than the secondary memory. In addition, its memory capacity is always smaller and much more limited than secondary memory. Primary memory is a part of the computer memory segment easily accessed by a processor.
Secondary Memory
The work of secondary memory is to store a high volume of data. Also known as memory & storage medium, secondary storage or backup memory & storage space is usually not accessible by the processor or personal computer. Nevertheless, it has a highly efficient storage capacity that saves many data in gigabytes and terabytes.
Secondary storage also refers to tertiary storage devices that store data and programs permanently or temporarily. They provide an extra efficient storage medium, hence less critical compared to primary memory & tertiary storage devices. Secondary memory is volatile, and unlike primary memory, it processes data slowly. Besides, the computer will still run even without secondary memory.

Secondary storage; semiconductor modules of dynamic random access memory, hard disk drives
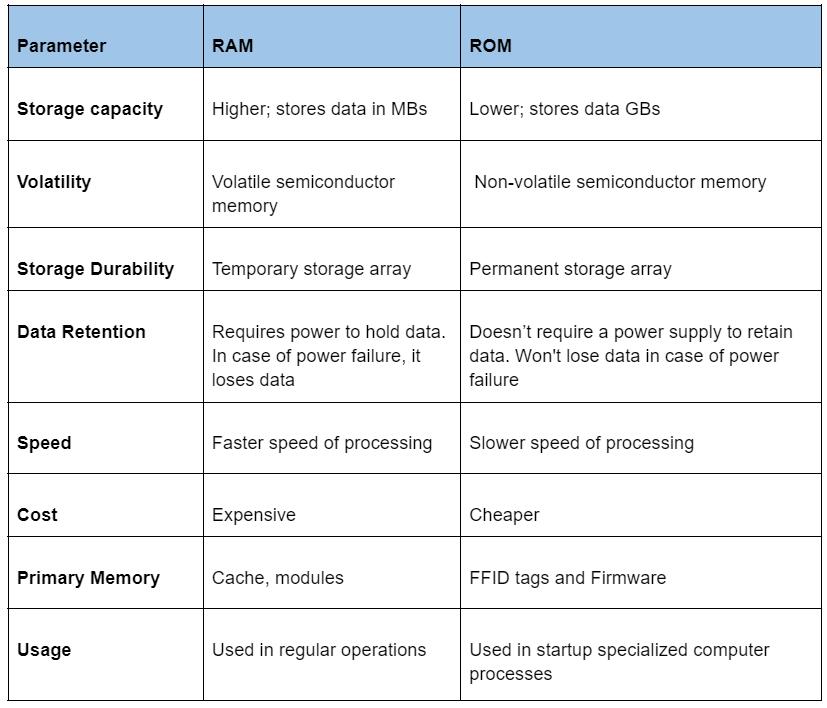
Primary Memory: ROM vs. RAM Comparison Chart
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
Why Computer System Need Primary Memory
Primary storage devices are high-speed. Its internal memory has a format structure that minimizes time proximity for the ready process to enhance system efficiency. The access time proximity in primary memory is much less than in secondary memory and more significant than in cache memory. It's about 200 times faster than a secondary storage device.
Reducing access time proximity for a ready process requires a strategic approach, including:
- The secondary memory isn't accessible by a processor or CPU directly.
- The secondary auxiliary storage stores all large files, data, and programs hence providing quicker access time per byte.
- The entire ready-to-be-executed processes load in the primary memory. It enables the CPU to optimize system performance and access those processes efficiently.
- The primary memory is more minor and accessible by the CPU directly. As a result, it enhances the execution of load processes in regular operating systems.
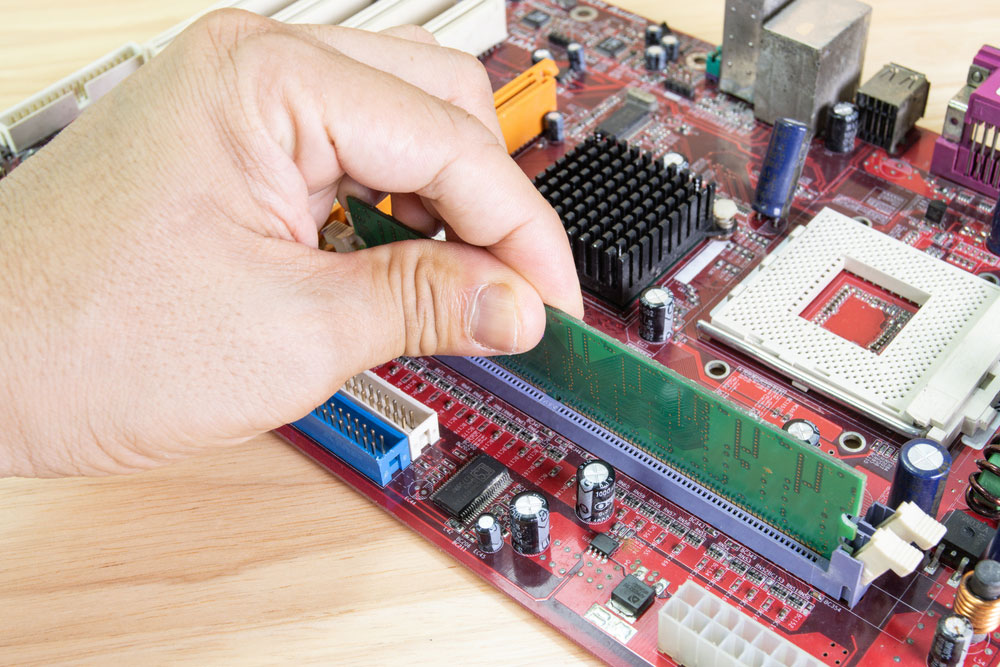
The technician is installing RAM on the motherboard Computer.
Classification of Primary Memory
There are two types of Primary Memory; RAM (Ram Access Memory) and ROM (Read Only Memory).
Read-Only Memory
ROM stores all the unaltered or unchanged data permanently, making it a non-volatile primary holographic storage memory. ROM includes data such as the algorithm required by OS and programs running on the booting system. It stores content and scientific applications such as mathematical tables, firmware, and boot programs pre-stored during the manufacturing stage. Even when there is a power failure, ROM still holds the content. Modern computers with storage capacity come with Flash millions of memory cells that store BIOS Firmware rather than ROM since it enhances updating versions.
Types of ROM
ROM consist of the following subdivisions:
a). PROM (Programmable ROM): With PROM, the user buys a device with a blank memory and stores the content using a device known as PROM Programmer. Therefore, the user can modify PROM. Once the user writes the desired content, it can't be altered. When the content is ready, it gives time and flexibility to verify and burn data post-manufacture.

Flashcard near old memory heap
b). EPROM (Erase and Programmable ROM): With ROM, the initial content reprograms and erases once you expose EPROM to UV radiation. It dissipates ROM change after exposing them to UV light, enabling content rewriting. Nevertheless, using the Electrical signal processing unit to erase data is much easier than using the UV rays procedure.
c). EEPROM (Electrically Erasable and Programmable ROM): With EEPROM, you can change the initial content by erasing it through automatic processing. Nevertheless, you can only erase one byte at a time. Therefore, it's always slow automated processing to reprogram with EEPROM.
d). MROM (Masked ROM): With MROM, you can't alter the written content since it's pre-programmed and hardwired.
Random Access Memory
RAM is a high-speed flash storage component also referred to as cache memory. It's the main computer system memory that stores devices requirements and permits the device to access data right away. In all the systems, automatic processing requires execution loads in the RAM. The CPU processes the RAM according to the program's instructions. For instance, by clicking on applications such as browsers, the operating system will load the browser code into RAM. Afterward, the CPU executes the application, opening up the browser. RAM is volatile; therefore, once you shut down your system, you will lose all the temporary stored memory.

USB flash disk
Types of RAM
RAM categorizes into two groups based on their behavior.
DRAM (Dynamic RAM): With dynamic, volatile semiconductor Random-Access memory, for you to retain data, you have to keep on refreshing it periodically. In addition, the electrical charge keeps leaking from DRAM and capacitors, requiring charging frequently. In the DRAM semiconductor memory chip, each million memory cell holds various data in bits. The memory controller will then rewrite the data once it requires reading it by refreshing constantly. The whole process takes time, making the SRAM faster than DRAM.

Two CPUs with RAM
SRAM (Static RAM): With this type of memory, data remains static; this doesn't need refreshing at any given time. Provided there is constant power flow, you can use SPRAM. It uses sequential circuits to store everything, such as a flip-flop, making it pretty fast. Usually, users prefer SRAM when processing speed is of utmost priority considering its high cost. SRAM works as cache listed in L3 or L2 values in the CPU, generally 1MB to 16MB.
Types of Secondary Memory
SSD: Solid-State Drive
SSD is a non-volatile storage hardware device that can improve the speed of your modern computer hence enhancing its overall performance. It stores and accesses data, and it's an effective substitute for typical hard optical drives. It's a great fit for laptops and modern computers with theoretical storage capacity. Also, it's suitable for notebook flash storage and tablets. They don't need an ample storage array and consume less power.
HDD: Hard Disk Drive

Internals of SATA hard disk drive
Hard disk storage usually stores large digital data storage amounts using a magnetic medium. Also known as magnetic auxiliary storage devices, hard disk storage data accessing power is slow, hence using RAM with high data retrieving power.
Flash Drives
Flash drives small portable devices that enable you to rewrite, delete and store data efficiently. Also known as USB built-in drives, pen built-in drives, or thumb built-in drives, they are the popular type of secondary offline storage devices. To robotic-access storage devices' data, it carries; you only need to plug it into your PC's USB port.

Flash drives are used to store data from computers.
NAS: Network-Attached Storage
NAS carries traditional mass storage, which you can access anytime if you have an Ethernet connection. It's a specialized file server that supports high-end applications, including analytics, 3D animation, and rendering.
SAN: Storage Area Network
SAN stores data in the block-level storage medium. It takes away tertiary storage device malfunction from the server creating a central data pool. Nevertheless, it doesn't depend on LAN (Local Area Network). The block-level stored data doesn't link to the file storage to libraries, but it's controlled by the operating system. As a result, SAN is the best choice for laid-back database hierarchical storage management.
Tertiary Memory: Cloud Storage
Tertiary memory & storage is the most common nowadays. It's an assortment of networked storage hardware that offers numerous computing features designed as virtual services. Though untouchable, you can control it remotely. It is an excellent option for constantly saving and accessing large data amounts, mainly for large organizations.

Cloud computing and storage
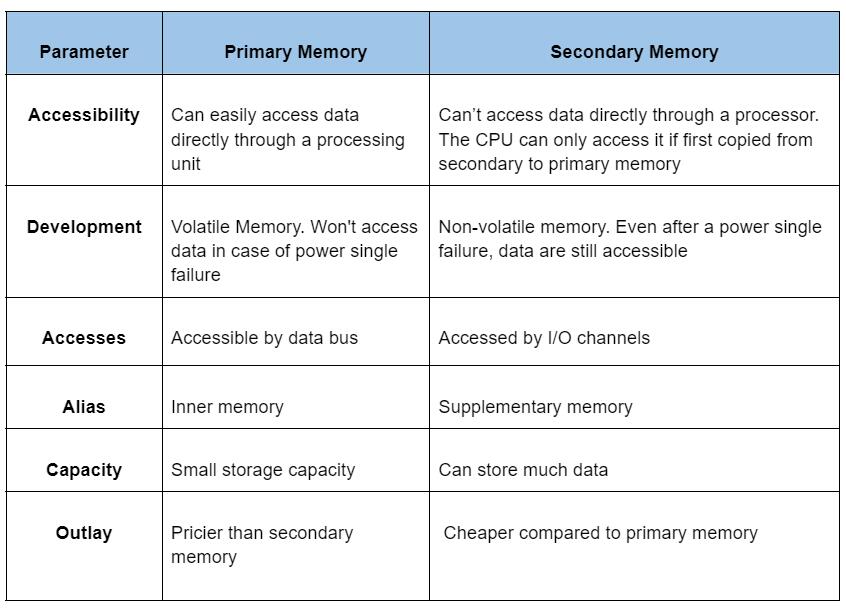
Primary Memory Vs. Secondary Memory
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!