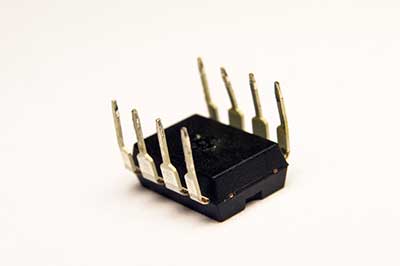
When working with an HDI board or even a conventional PCB (Printed Circuit Board), holes must be screwed shut.
These holes include an open pit, a countersunk hole, a blind hole, and a counterbore hole.
Often, we confuse a countersink for a counterbore and vice versa. It is why we need to understand the working principles of each of them entirely.
The countersink and counterbore are holes that require different types of specific fixtures.
They are so diverse that ignorance makes using one instead of the other hazardous.
Therefore, the similarities and purposes are significant to understand the difference between the two holes.
Let us learn how to effectively fix the PCB without worrying about falling off or loosening the accessories.
Contents
- 1、Countersink VS Counterbore
- What is Countersink?
- What is Counterbore?
- Similarities and Differences Between Them
- The counterbore is typically used for a single purpose while
- 2、 Countersink VS Counterbore Symbol
- What does a countersink symbol look like?
- What does a counterbore symbol look like?
- 3、Countersink VS Counterbore Drill Bits
- What to Do When Using a Countersink Drill Bit
- 4、When to Use Countersink and Counterbore in PCB
- Limited Space and Mounting Security
- 5、Countersink VS Counterbore PCB Applications
- Countersink VS Counterbore--What are They Used for?
- 6、Countersink VS Counterbore Dimensioning Techniques
- How To dimension a countersink and a counterbore
- 7、Countersink VS Counterbore--Conclusion
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Please email [email protected] for details.
1、Countersink VS Counterbore
Before comparing them, let's highlight what a countersink and a counterbore are.
What is Countersink?
A countersink is a cone-shaped hole that is bored into a PCB. This hole allows a flathead screw or fastener to fit correctly once installed.
What is Counterbore?
A counterbore is more of a cylindrical flat-shaped hole. The hole formed has a flat bottom, allowing a screw or fastener with a flat underside to fit.
Also, the instrument used to create this feature is known as a counterbore. The word will be used interchangeably.
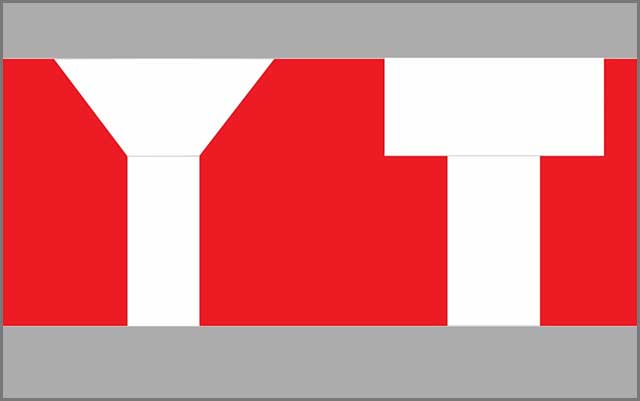 Image 1:Countersink VS Counterbore
Image 1:Countersink VS Counterbore
Similarities and Differences Between Them
The practice of making a countersunk hole is known as countersinking. Now, a countersunk hole may come in different sizes of angles.
It includes 60, 82, and 90 degrees standard sizes alongside the less popular 100, 110, and 120 degrees.
However, the most frequently used degrees are 82, 90, and 100.
While the only angle applicable to a counterbore is a vertical zero degree, it is just as effective as a countersink.
It is important to note that when working with a wooden surface, if you fail to countersink first but end up forcing the screw into this surface, not only will the wood's stability and strength be compromised, but your work will consequently be an eyesore.
Because the wood fibers will crack and become dented if not wholly damaged, it is much easier to counterbore a wooden surface because counterboring does not require precision and accuracy in the angles.
Also, in a counterbore, all the hole needs are a screw with a flat underside or a socket head that can fit with the surface or washer.
The counterbore is typically used for a single purpose while
Countersinks, due to their different angles, have other purposes.
A counterbore is often similar to a small coaxial hole enlargement, while a countersink is a conical version.
Use it when you don't want the fixture's head, or screw the bolt forward from the HDI surface you are working on.
On the other hand, countersunk holes have different styles because of their different angles.
With countersinking, all your screws can have the same depth.
2、 Countersink VS Counterbore Symbol
In drawing or design, symbols are used as a representation of the actual material or technique.
With characters, there is room for dimensional consistency and tolerance of specifications.
Also, it is much faster and even easier to write the symbol of material or quantity instead of spelling it out with actual words on a drawing.
It is not only against drawing protocol but will also make your work clustered.
Symbols represent basic protocols in drawing, design, or mathematics.
In a building or house plan drawing, symbols are used to convey information faster.
Here, the character of a countersink and a counterbore is duly represented.
It is often side by side with the diameter symbol and accompanied by a numerical value.
What does a countersink symbol look like?
A countersink symbol resembles the letter V. When you think about it, looking at a countersunk hole from the side, it resembles the letter V.
What does a counterbore symbol look like?
The symbol of a counterbore has been likened to an incomplete square with an opening at the top.
In technical drawing, this symbol was formed by taking the side view of the countersink and counterbore holes.
Both symbols are used in drilling designs. The diameter emblem shows how wide or deep a hole is meant to be.
A builder interprets these designs based on the information provided in these designs.
A counterbore symbol defines counterboring operations, while a countersink is for countersinking fastening operations.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Please email [email protected] for details.
3、Countersink VS Counterbore Drill Bits
You could create several holes when using a drill bit, depending on the required diameter and the thickness of the material.
But they are hole drills for a counterbore and a countersink, so they create the process.
The drill bits are the instruments used for drilling or creating a countersink hole or a counterbore into the surface of a material, a print circuit board, or a PCB.
Both types of holes use different materials for their fabrication.
Ultimately, the aim is to create a spot where a screw or fastener can sit flush within the washer or workpiece.
It is done to hide the entire length and axis of the fastener or screw in the countersunk hole or counterbore.
Different materials are used for fabrication because of the difference in their cavity (one is flat, and the other is angled).
For counterboring, a cylindrical hole is bored into the material's surface. This hole has a large diameter at the head and a smaller one below.
The screw or fastener is meant to sit correctly and prevent the two surfaces from separating when joined.
The larger side of the hole fits the fastener's head, while the smaller one accommodates its shaft.
However, countersink drill bits come in different styles and sizes to accommodate the different angles and other projects.
The picture above has about four different types of countersink drill bits.
These are the fluted bits, the cross-hole countersink, the rocker pro, and the flip-style countersink.
 Image 2: Countersink VS Counterbore
Image 2: Countersink VS Counterbore
What to Do When Using a Countersink Drill Bit
When using a countersink drill bit, it is essential to correctly match the drill's size to that of the screw.
A countersunk hole that is too large will swallow the head of the screw or fastener, while a spot that is too small will not fit the head of the screw, leading to a loosely fitted mount.
What happens if you forcefully drive the screw into the hole?
Nevertheless, the surrounding materials will be damaged if you forcefully drive the fastener into the hole. It goes for both HDI and wood surfaces.
Hence if your spot is shallow, the screw will not flush with the body, and if it's too thick, the screw will remain shallow inside.
Hence, it is essential to take measurements to make drill holes that fit the screws.
To get the appropriate measurement, adjust your countersink settings.
It is the countersink size, drill bit depth, and the center's stop location.
Even with these adjustments, it is advisable to practice on a piece of scrap material before drilling onto the entire surface to ensure you have the right measurements.
Lastly, to prevent chatter, do not drill too fast. This will cause uneven patterns in your material surface, and your fastener will not fit into it, causing you to either abandon the material or start all over again.
4、When to Use Countersink and Counterbore in PCB
Now we've established the basics of a counterbore and a countersink hole, let's see when it can be used in a PCB.
Although both fixtures are usually for firmer surfaces like wood and metals, they can still be used on a printed circuit board.
Like most circuit boards, a PCB has holes and the method of drilling each hole matters.
Some of these holes are screw holes, used as an opening to attach the PCB to an application.
The difference in the type of available screws determines the holes you will drill onto the PCB, either a countersunk hole or a counterbore hole.
 Image 3: Countersink VS Counterbore
Image 3: Countersink VS Counterbore
Limited Space and Mounting Security
If you're running out of space in your device but want additional features on it to increase your device's flexibility, you can drill a conical countersink hole into the PCB.
This hole is designed to fit a typical screw with a flat head, requiring more precision than a counterbore hole.
Once the screws are flush with the board, it becomes easier to fit the PCB into the required device, either a smartphone or a watch.
However, although easy to fabricate, a counterbore is not usually the best choice for a PCB.
It is where the countersink comes in. A countersunk hole keeps the board's surface smoother, and when done correctly, there is no interference with the arrangement of the board's design.
However, if you require a more secure PCB mounting other than conserving space or going for a smoother design, go for counterbore holes.
These holes are usually large enough to accommodate socket fixtures; hence, the screws from them will create a more secure attachment.
On the other hand, if you want to conserve space, then go for a countersink hole.
5、Countersink VS Counterbore PCB Applications
Usually, a printed circuit board is mounted via a screw in a hole.
A countersink or a counterbore hole can be used if you need a more evident fixture appearance and a safer installation.
This drilling process is often done by hand through automated equipment.
Drill a counterbore using a grub screw; the hole creates a perfect foundation for the screw to overlap and fit perfectly into the hole.
Countersink VS Counterbore--What are They Used for?
A countersunk hole in a PCB creates room for a clean installation and is ideal for tight-fitting applications in small devices.
PCB countersink applications are found in mobile phones and other small wearable devices.
A counterbore offers a cylindrical fit to the screw. It is flat-bottomed and is cut to allow a socket cap screw to be used.
This hexagon socket screw has a hex head and needs to be mounted safely on the PCB.
It can be found in washers and other electronic devices that require tight and secure fittings.
 Image 4: Countersink VS Counterbore
Image 4: Countersink VS Counterbore
6、Countersink VS Counterbore Dimensioning Techniques
In the drawing, dimensioning is mandatory. It is the only way a builder or technician can apply the drawing in real life.
Dimensioning reveals the size, type, and texture of materials used during construction or fabrication.
In this context, dimensioning technology expresses countersunk and counterbore in a design or chart specified on a diagram through dimension symbols and abbreviations.
They indicate the surface type's form and offer no restrictions to its fabrication method.
These dimensions are usually represented as a note and preceded by the size through the holes.
How To dimension a countersink and a counterbore
For a countersink, the angular sides are recessed to compensate for the head of the flathead fixtures, which could be screws, rivets, bolts, or other similar items.
When drawing, Given surface diameter and an angle, and for a counter drilled hole, the diameter, depth, and included rise are also given.
The flat-bottomed and cylindrical part for a counterbore permits the fastener's head to lie in the recessed portion.
The diameter, depth, and corner radius are given and specified when drawing and dimensioning this.
In a few situations, the thickness of the remaining shaft can be dimensioned in place of the center.
Both holes could be dimensioned in a rectangular or a Polar coordinate form.
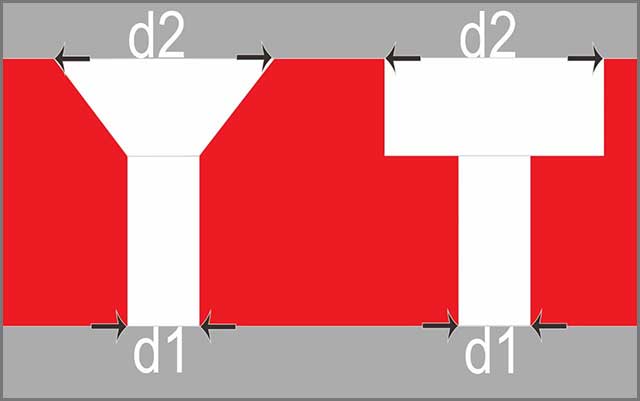 Image 5: Countersink VS Counterbore
Image 5: Countersink VS Counterbore
7、Countersink VS Counterbore--Conclusion
Both counterbore and countersink holes are used with corresponding screws to attach to different materials. Although not common, using this as a fixture for a print circuit board works similarly. We've seen that a countersink is a cone-shaped hole, while a counterbore is more cylindrical.
In this piece, we have highlighted the differences between the counterbore and a countersink, their corresponding similarities, their definition, and the working principle of both holes.
The type of screws that fit into a counterbore and a countersunk hole is equally known as counterbores and countersinks, as the term can be used interchangeably.
We have also seen the difference in their fabrication method using the different drill bits for each hole type.
Also, for this paper, we highlighted when we could use a countersink and a counterbore in a print circuit board (PCB) and their related applications and uses.
Lastly, to ensure one can see and recognize both holes on the paper, we have highlighted their different symbols and the dimensioning techniques used for each hole type.
However, you can contact us for more information concerning the counterbore, countersink hole, fixtures, PCB, and HDI boards.
Alternatively, if you are having problems with your current counterbore or countersinking materials like drill bits, screws, or bolts and you would like to change them, all you'll need to do is to head over to our website and place an order for what you require, and we'll get it to you.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Please email [email protected] for details.