Various components come together in the realm of electricity to complete a circuit. For two devices that have similar functions, it is no surprise that they are often mistaken. Although the difference between a potentiometer and rheostat is not much, it becomes easier to know with further examination. The essence of this guide is thus to put in perspective these differences.
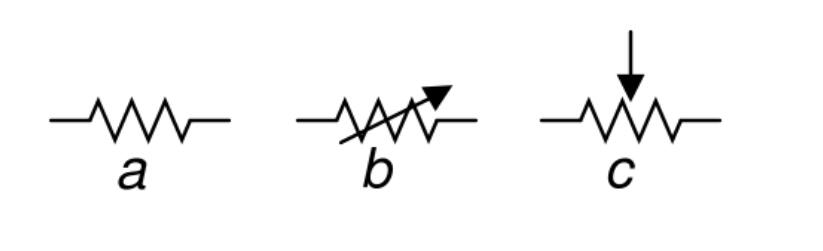
(Circuit Symbol A for Resistor, Symbol B for Rheostat,, and Symbol C for Potentiometer)
Contents
- What is a Potentiometer?
- Types of Potentiometers
- Applications of Potentiometer
- What is a Rheostat
- Types of Rheostats
- Linear Rheostat
- Rotary Rheostat
- Preset Rheostat
- Applications of Rheostat
- Difference Between Potentiometer and Rheostat
- How to choose Between Potentiometer and Rheostat
- Maximum Resistance
- Wiper Resistance
- Taper Style
- Power Rating
- Tolerance and Hysteresis
- Conclusion
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Please email [email protected] for details.
What is a Potentiometer?
The potentiometer, commonly called POT for short, is a three-terminal variable resistor that regulates circuit resistance. Most times, potentiometers come with a maximum resistance inscription and an adjustable variable divider, and thisthis feature is easily modified with a flexible shaft that runs up from the center.
Also, most potentiometers have a resistive element made from graphite or other factors. Potentiometers likewise function as measuring tools for displacement in any direction. Typically, systems use potentiometers to change the voltage or to provide a variable voltage source.

(Image of a Potentiometer)
Types of Potentiometers
Potentiometers are available in two forms which are logarithmic potentiometers and linear potentiometers. The logarithmic and linear potentiometers are both three-terminal devices. On the one hand, the logarithmic potentiometer measures the angular position while the linear one measures the linear function. Majorly, electronics use a digital potentiometer.
Applications of Potentiometer
- Primarily, a potentiometer works in variable supply voltage division.
- Also, potentiometers are measuring devices.
- In an audio device and television control.
- Another common application is as a position transducer in joysticks.
- In circuitry, the potentiometer regulates the input voltage.
- Another function of the potentiometer is as a displacement transducer.

(Potentiometer as an electronic control unit)
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Please email [email protected] for details.
What is a Rheostat
To begin with, rheostats are two-terminal variable resistors that divide voltage in circuits that need resistance control. You can use rheostats where there’s a demand for variable control with higher voltages. For example, large industrial machines, electric motors,, etc. The primary function is to maintain and control the flow of current in an electrical circuit.
Furthermore, the rheostat has two terminals, a resistive material,, and a movable wiper. The majority of rheostats are wire-wound, with a long conducting material spiraled around them. It either uses a metal wire or ribbon and a conductive liquid or carbon as the resistance element.
Unlike a potentiometer, a rheostat does not require a connection of double terminal ends to function correctly. While one of the ends of the airport works, the other can stay open.
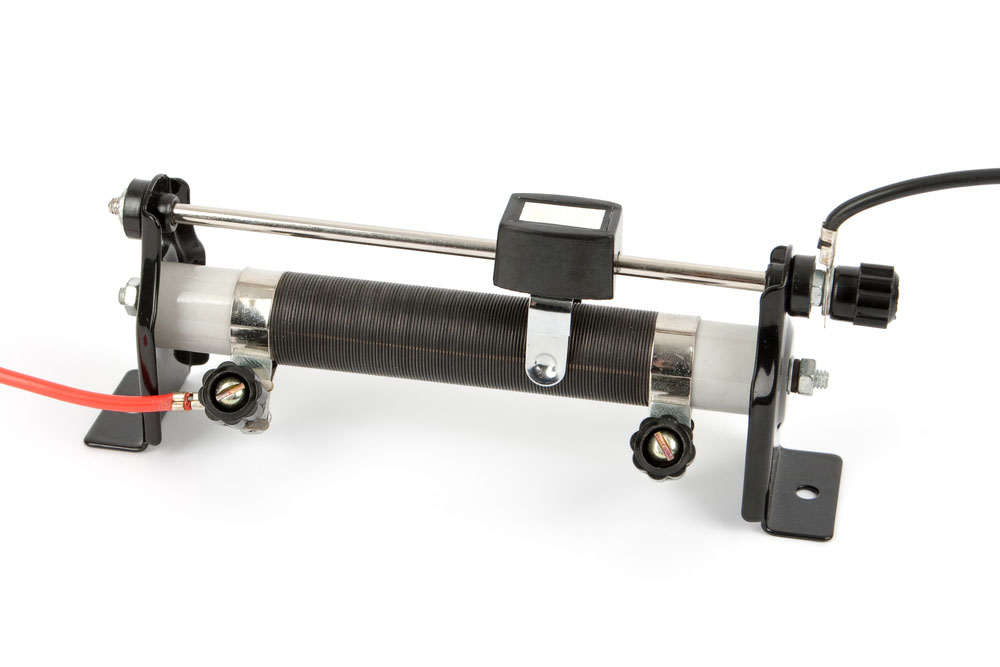

(Image of a sliding Rheostat)
Types of Rheostats
The types of rheostats are in three categories: linear, rotary, and preset.
-
Linear Rheostat
A linear rheostat commonly found in laboratory applications consists of a wire-wound linear resistive path on which the slide moves. Although they have two fixed terminals, only one functions, while the other works with the slider.
-
Rotary Rheostat
Just as the name implies, the rotary rheostat contains a rotational resistive path and a shaft that houses the wiper. The rotary types of rheostat work similarly to a linear rheostat.
-
Preset Rheostat
Preset rheostats are sometimes known as trimmer rheostats since they have two terminal trimmers. These rheostats are in calibration circuits and small in size.

(Variable Resistor - Rheostat)
Source: https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Stripped_wire_rheostat.jpg
Applications of Rheostat
- Rheostats function as regulators for volume in audio devices.
- Temperature regulators found in ovens and heaters are another application of Rheostats.
- Dim lights and other power control devices make use of Rheostats in reducing their intensity.
- Rheostats also regulate the speed of motors.
- Similarly, audio equipment makes use of rheostats to regulate volume.
- Also, employed for calibration and tuning in systems.
- Lastly, medical equipment and X-ray machines use rheostats.

(Rheostat in Use as a Light Dimmer)
Difference Between Potentiometer and Rheostat
In this section, the potentiometer vs.. rheostat goes head-to-head. See both in terms of different parameters.
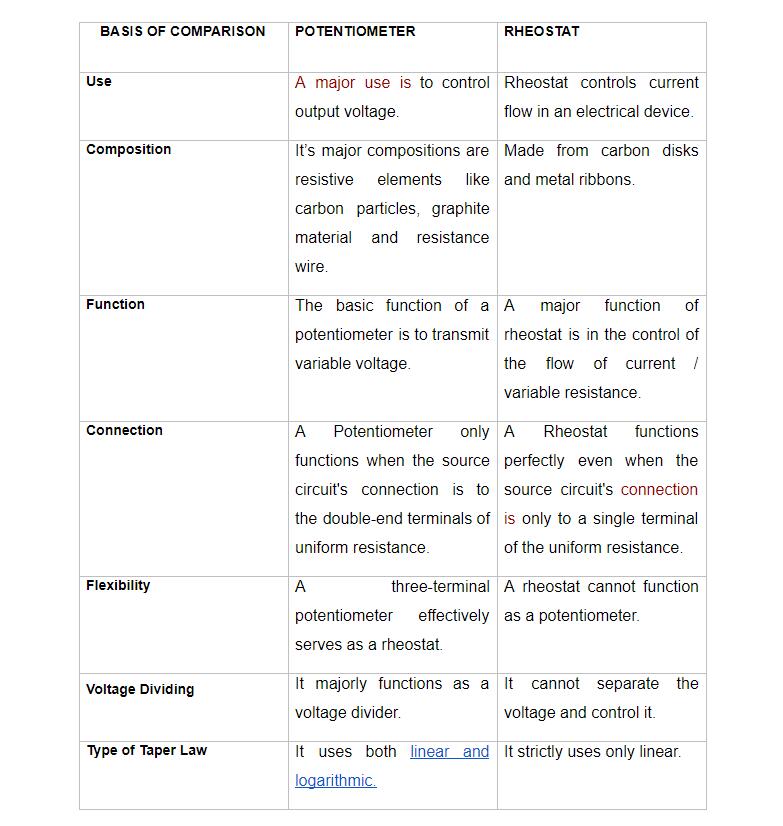
How to choose Between Potentiometer and Rheostat
When choosing between these two components, it’s imperative to note that they differ slightly in terms of the following specifications.
-
Maximum Resistance
This parameter determines the voltage that gets to the load. The potentiometer has a maximum resistance of 1 megaohm, while the rheostat has ten megaohms. For this purpose, the rheostat works better as it is the potentiometer with infinite resistance.
-
Wiper Resistance
To ensure an accurate supply of current, the wiper resistance in a rheostat must be meager. On the other hand, the wiper resistance is negligible in a potentiometer, and thisthis is because it is always tiny in comparison to the load resistance. As a result, the potentiometer is your go-to for better wiper resistance.
-
Taper Style
This parameter depicts how a device’s resistance changes when the broader shifts. The potentiometer uses both making it the better candidate.
-
Power Rating
A Rheostat functions appropriately, whether in a high or low power application. A potentiometer, however, only operates better in a low-power application. For this reason, the rheostat is a better option in this category.
-
Tolerance and Hysteresis
The resistance tolerance of both components varies due to the helical structure and hysteresis, and this variance is usually between 10 and 20 percent. So, it is a tie here.
Conclusion
Above all, it would appear that though similar, the Potentiometer and Rheostat have their differences. In truth, both are variable resistors for monitoring current and voltage in electronic circuits. However, they are also quite distinct and do not always replace each other perfectly.
Therefore, the difference between Potentiometer and Rheostat might not be a pointer to the better option between them, and thisthis is because they're both favored in various applications. If you require any clarification, you can reach us here.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Please email [email protected] for details.