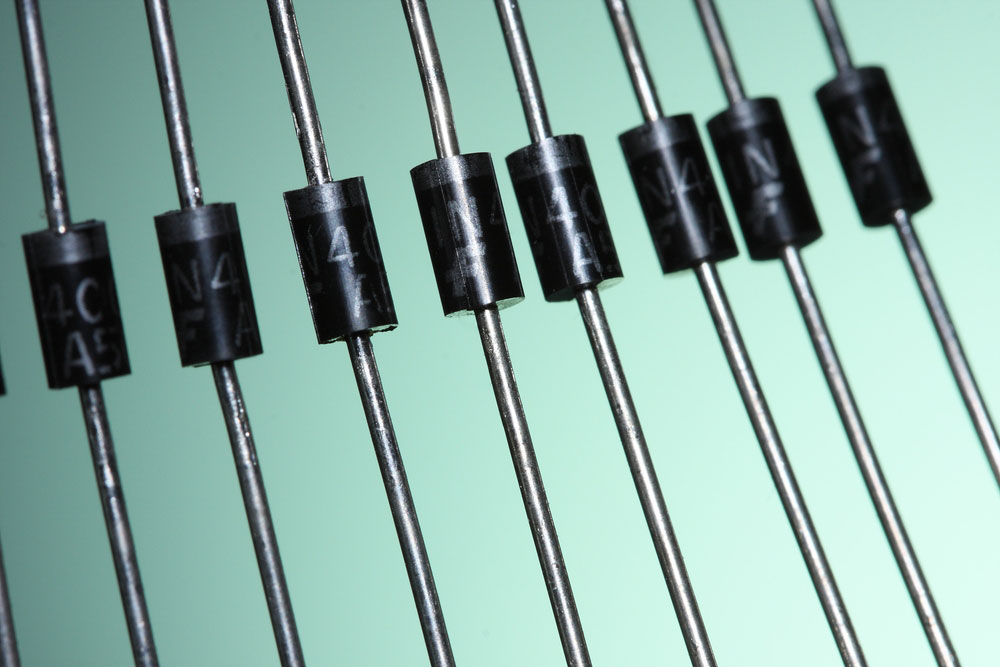
Ever sat in an electronics class, or you are just an electronics enthusiast, you must have come across this term diode. However, you have at one time come across a diode that is unlike the Zener diode or the Silicon diode its symbol or properties. This diode is also called the Schottky diode. In a circuit board where you will be directing current, you will need a lot of knowledge on Schottky diodes. To complete your circuit board, you will also need the Schottky diode and other components for a more practical approach. In this article, we will look at the Schottky diode 1n5822.
(A photo of various types of Schottky diodes)
SOURCE: WIKIPEDIA
Contents
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Please email [email protected] for details.
1. What is 1n5822?
(A picture of the 1n5822 diode)
The Schottky 1n5822 is one of the three Schottky diodes called the Hot-carrier diode. Unlike the 1n5820 and the 1n5821, the 1n5822 accommodates more reverse and forward voltage to pass through it. The 1n5822 Schottky diode has a Maximum repetitive peak reverse voltage(VRRM) of 40V and a Maximum instantaneous forward voltage (VF(1) ) of 0.525V.
The 1n5822 diode can have these qualities because it uses a semiconductor combined with metals such as molybdenum, silicides, tungsten, chromium, and platinum. 1n5822 is also used in high-speed switching applications operating at lower currents.
2. 1N5822 characteristics
- Contains Guarding, which helps in surge or overvoltage protection.
- Very minimal conduction of power losses.
- High-speed switching.
- Forward voltage drop is minimal. The voltage drop is primarily minimal because it is made of semiconductors.
- High-capacity forward surge.
- Operates with a high frequency.
- Has a Solder dip of 275 °C max. 10 s, per JESD 22-B106.
- It comes packaged in DO-201AD.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Please email [email protected] for details.
3.1 Technical Specifications of N5822
- Maximum peak repetitive reverse voltage V (VRRM) of 40 Volts from the power source.
- Maximum root means square (RMS), voltage (VRMS) of 28 Voltage rating.
- DC voltage blocking (VDC) of maximum 40 Volts.
- Non-repetitive reverse peak voltage (VRSM) of 48 Volts.
- Maximum average rectified forward current rating at 0.375" (9.5 mm) lead length at TL = 95 °C (IF(AV)) of 3.0A.
- Peak forward current surge, 8.3 ms half of the sine-wave imposed on the rated load (IFSM) of 80A.
- Temperature ranges for the storage and operating junction (TJ) of between -65 to +125 °C.
- The maximum forward instantaneous voltage of (VF(1) ) of 0.525V when the power supply is at 3.0V and 0.950V when the power supply is at 9.4V.
- At the rated DC blocking voltage, the maximum average reverse current (VR(1) ) of an average 2.0 mA under a wide operating temperature range of 25 °C and 20 mA under a temperature of 100 °C.
3. 1N5822 Pin Configuration
Like the Zener and Silicon diodes, the Schottky diode has just two pins, differentiated mainly by the color band around each pin. Therefore we will be looking at both pins, how to know them, and their functionalities.
(A picture of the Anode and Cathode pin configuration)
(2D representation of the Anode and Cathode)
SOURCE: WIKIPEDIA
- Anode
- Has no coloring or bands around it.
- It allows the current to enter the diode through it; hence it has positive polarity.
- Cathode
- It has a greyish-silver coloring or band around it.
- It allows the current to exit the diode; hence it has a negative polarity.
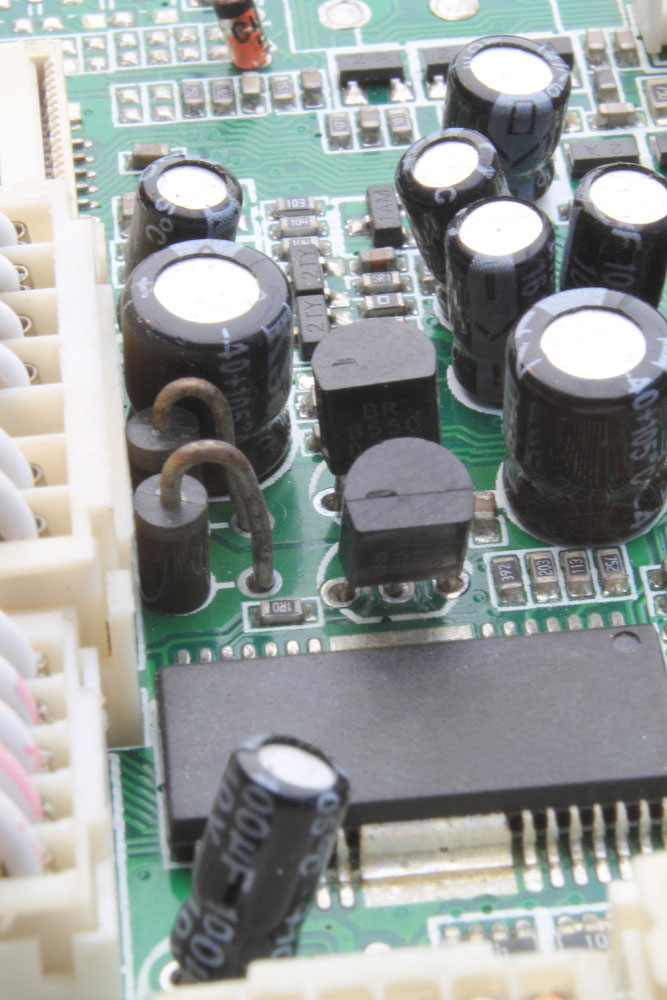
4.1n5822 Application
(A picture of a 1n5822 Schottky diode glued to the circuit board as one of its components)
- Often used in low-voltage and high-frequency inverters.
- Used in Freewheeling.
- Applied in DC/DC converters.
- To detect signals in circuit boards and appliances.
- Used as a polarity protection device in applications.
- Incorporated in logic circuits because of fast switching improving efficiency in applications.
- Incorporated in radio frequency appliances.
- Applied to control electronic charge.
- Used in photovoltaic systems.
- Used in fast-clamp diode switching applications.
5. Summary
In summary, the Schottky diode 1n5822 has a well-balanced role than the Silicon diode and the Zener diode. Its versatility produces less heat than other diodes due to its shallow forward voltage drop. This makes it a magnificent must-have diode in your Application. If you have any questions or compliments concerning this article, please contact us.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Please email [email protected] for details.